ב-Java, ריק הוא מילולי. הוא משמש בעיקר כדי להקצות ערך null למשתנה. ערך null אפשרי עבור מחרוזת, אובייקט או תאריך ושעה וכו'. איננו יכולים להקצות ערך null לסוגי הנתונים הפרימיטיביים כגון int, float וכו'.
בתכנות, בדרך כלל אנחנו צריכים לבדוק אם אובייקט או מחרוזת הם null או לא כדי לבצע עליו משימה כלשהי. על מנת לבדוק מחרוזת null, יש לנו כמה שיטות מוגדרות מראש של מחרוזת. הבה ניקח כמה דוגמאות לסוגי נתונים שונים כדי להבין כיצד נוכל לבדוק אם הם אפסים או לא.
חוּט
ב-Java, String יכול להיות null, ריק או ריק, וכל אחד מהם שונה.
1. מחרוזת ריקה היא אובייקט מחרוזת בעל ערך כלשהו, אך אורכו שווה לאפס. לדוגמה:
String str1 = ''
2. מחרוזת ריקה היא מחרוזת שהערך שלה הוא רווח לבן. אורכו תמיד גדול מ-0 ולא ריק ולא ריק. לדוגמה:
mvc java
String str2 = ''
3. למחרוזת null אין ערך והיא הופכת מחרוזת לאפס על ידי הקצאת a ריק מילת מפתח כערך עבורה. לדוגמה:
String str3 = null
על מנת לבדוק אם String הוא null או לא, אנו משתמשים באופרטור ההשוואה(==). בואו ניקח דוגמה שלו כדי להבין איך אנחנו יכולים להשתמש בו לבדיקת null.
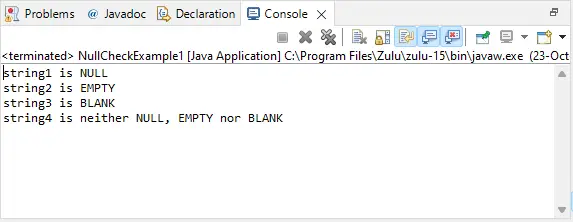
NullCheckExample1.java
// import required classes and packages packagejavaTpoint.javacodes; // create class NullCheckExample1 class to check whether a string is empty or null class NullCheckExample1 { // main() method start public static void main(String[] args) { // create null, empty, and blank strings String string1 = null; String string2 = ''; String string3 = ' '; String string4 = 'Test'; // check whether string1 is null, empty, or blank System.out.println('string1 is ' + checkNullEmptyBlank(string1)); // check whether string2 is null, empty, or blank System.out.println('string2 is ' + checkNullEmptyBlank(string2)); // check whether string3 is null, empty, or blank System.out.println('string3 is ' + checkNullEmptyBlank(string3)); // check whether string4 is null, empty, or blank System.out.println('string4 is ' + checkNullEmptyBlank(string4)); } // create checkNullEmptyBlank() method which check whether the string is empty, null or blank and return result to the main() method public static String checkNullEmptyBlank(String strToCheck) { // check whether the given string is null or not if (strToCheck == null) { return 'NULL'; } // check whether the given string is empty or not else if(strToCheck.isEmpty()) { return 'EMPTY'; } // check whether the given string is blank or not else if(strToCheck.isBlank()) { return 'BLANK'; } else { return 'neither NULL, EMPTY nor BLANK'; } } } תְפוּקָה:
כיצד לקרוא מקובץ csv ב-java
אובייקט תאריך ותאריך זמן
תאריך ותאריך זמן שניהם הם סוגי הנתונים הלא פרימיטיביים, כך שהם יכולים לאחסן ערך ריק. הבה ניקח דוגמה של אובייקט תאריך ושעה כדי להבין כיצד נוכל לבדוק אובייקט תאריך ריק או תאריך שעה.
NullCheckExample2.java
//import required classes and packages packagejavaTpoint.javacodes; importjava.text.ParseException; importjava.text.SimpleDateFormat; importjava.util.Date; importjava.util.Scanner; //create class NullCheckExample2 class to check whether the Date object is null or not public class NullCheckExample2 { // declare a variable of date type and initialize it with null public static Date d1 = null; public static Date finalResult; // main() method start public static void main(String args[]) { // declare a variable of type string that will store the user-entered date in string format String d2; // create scanner class object Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print('Enter Date in dd/mm/yyyy format:'); // take input from user and initialize variable d2 = sc.nextLine(); // close scanner class obj sc.close(); // create an instance of the SimpleDateFormat class for modifying the date object SimpleDateFormatobj = new SimpleDateFormat('dd/MM/yyyy'); // use try-catch to parse string to date try { finalResult = obj.parse(d2); } catch (ParseException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } // check whether date1 and date2 is null or not by using comparison operator if(d1 == null) { System.out.println('Date d1 is NULL.'); } if(finalResult == null) { System.out.println('Date d2 is NULL.'); }else { System.out.println('Date d2 is not NULL.'); } } } תְפוּקָה:

אובייקט ג'אווה
על מנת לבדוק אם אובייקט Java הוא Null או לא, נוכל להשתמש בשיטת isNull() של ה- חפצים מחלקה או אופרטור השוואה. ניקח דוגמה כדי להבין כיצד אנו יכולים להשתמש בשיטת isNull() או באופרטור ההשוואה לבדיקת null של אובייקט Java.
NullCheckExample3.java
// import required classes and packages packagejavaTpoint.javacodes; // create NullCheckExample3 class to check whether Java object is null or not public class NullCheckExample3 { // main() method start public static void main(String[] args) { // create instance of User2 User2 userObj = new User2(); // get data of User2 by calling User1 firstUser = userObj.getFirstUser(); // check whether firstUser is null or not if (firstUser == null) { System.out.println('Object is Null'); } else { System.out.println('Object is not Null'); // set name for user1 firstUser.setName('Paul'); System.out.println(firstUser.getName()); } } } // create User1 class having a name attribute class User1 { // declare name variable String name; // getter for getting name of User1 public String getName() { // return name of User1 return name; } // setter for setting name of User1 public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } } // create class User2 having variable of type User1 class User2 { User1 obj; // getter to get object of User1 public User1 getFirstUser() { returnobj; } } תְפוּקָה:

NullCheckExample4.java
// import required classes and packages packagejavaTpoint.javacodes; importjava.util.Objects; // create NullCheckExample3 class to check whether Java object is null or not public class NullCheckExample4 { // main() method start public static void main(String[] args) { // create instance of User2 User2 userObj = new User2(); // get data of User2 by calling User1 firstUser = userObj.getFirstUser(); // check whether firstUser is null or not if (Objects.isNull(firstUser) ){ System.out.println('Object is Null'); } else { System.out.println('Object is not Null'); // set name for user1 firstUser.setName('Paul'); System.out.println(firstUser.getName()); } } } // create User1 class having a name attribute class User1 { // declare name variable String name; // getter for getting name of User1 public String getName() { // return name of User1 return name; } // setter for setting name of User1 public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } } // create class User2 having variable of type User1 class User2 { User1 obj; // getter to get object of User1 public User1 getFirstUser() { returnobj; } } תְפוּקָה:

