ב-C++, ירושה היא תהליך שבו אובייקט אחד רוכש את כל המאפיינים וההתנהגויות של אובייקט האב שלו באופן אוטומטי. בצורה כזו, אתה יכול לעשות שימוש חוזר, להרחיב או לשנות את התכונות וההתנהגויות המוגדרות במחלקות אחרות.
ב-C++, המחלקה שיורשת את האיברים של מחלקה אחרת נקראת מחלקה נגזרת והמחלקה שהחברים בה עוברים בירושה נקראת מחלקה בסיסית. המחלקה הנגזרת היא המחלקה המיוחדת למחלקה הבסיסית.
יתרון בירושה ב-C++
שימוש חוזר בקוד: עכשיו אתה יכול לעשות שימוש חוזר בחברי כיתת ההורים שלך. לכן, אין צורך להגדיר שוב את החבר. אז נדרש פחות קוד בכיתה.
ההבדל בין גיגה-בייט למגה-בייט
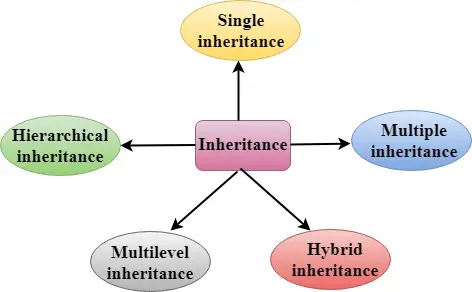
סוגי ירושה
C++ תומך בחמישה סוגי ירושה:
- ירושה בודדת
- ירושה מרובה
- ירושה היררכית
- ירושה רב-שכבתית
- תורשה היברידית
שיעורים נגזרים
מחלקה נגזרת מוגדרת כמחלקה הנגזרת ממחלקת הבסיס.
ההבדל בין אריה לנמר
התחביר של המחלקה הנגזרת:
|_+_|במקרה הנ'ל, הפונקציה של המחלקה הנגזרת עוקפת את השיטה של מחלקת הבסיס. לכן, קריאה לפונקציה display() פשוט תקרא לפונקציה שהוגדרה במחלקה הנגזרת. אם ברצוננו להפעיל את פונקציית המחלקה הבסיסית, נוכל להשתמש באופרטור רזולוציית המחלקה.
int main() { B b; b.display(); // Calling the display() function of B class. b.B :: display(); // Calling the display() function defined in B class. } ירושה היברידית C++
ירושה היברידית היא שילוב של יותר מסוג אחד של ירושה.

בואו נראה דוגמה פשוטה:
#include using namespace std; class A { protected: int a; public: void get_a() { std::cout << 'Enter the value of 'a' : ' <>a; } }; class B : public A { protected: int b; public: void get_b() { std::cout << 'Enter the value of 'b' : ' <>b; } }; class C { protected: int c; public: void get_c() { std::cout << 'Enter the value of c is : ' <>c; } }; class D : public B, public C { protected: int d; public: void mul() { get_a(); get_b(); get_c(); std::cout << 'Multiplication of a,b,c is : ' < <a*b*c<< std::endl; } }; int main() { d d; d.mul(); return 0; < pre> <p>Output:</p> <pre> Enter the value of 'a' : 10 Enter the value of 'b' : 20 Enter the value of c is : 30 Multiplication of a,b,c is : 6000 </pre> <h2>C++ Hierarchical Inheritance</h2> <p>Hierarchical inheritance is defined as the process of deriving more than one class from a base class.</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/62/c-inheritance-7.webp" alt="C++ Inheritance"> <p> <strong>Syntax of Hierarchical inheritance:</strong> </p> <pre> class A { // body of the class A. } class B : public A { // body of class B. } class C : public A { // body of class C. } class D : public A { // body of class D. } </pre> <p>Let's see a simple example:</p> <pre> #include using namespace std; class Shape // Declaration of base class. { public: int a; int b; void get_data(int n,int m) { a= n; b = m; } }; class Rectangle : public Shape // inheriting Shape class { public: int rect_area() { int result = a*b; return result; } }; class Triangle : public Shape // inheriting Shape class { public: int triangle_area() { float result = 0.5*a*b; return result; } }; int main() { Rectangle r; Triangle t; int length,breadth,base,height; std::cout << 'Enter the length and breadth of a rectangle: ' <>length>>breadth; r.get_data(length,breadth); int m = r.rect_area(); std::cout << 'Area of the rectangle is : ' <<m<< std::endl; std::cout << \\'enter the base and height of triangle: \\' <>base>>height; t.get_data(base,height); float n = t.triangle_area(); std::cout <<\\'area of the triangle is : \\' << n<<std::endl; return 0; } < pre> <p>Output:</p> <pre> Enter the length and breadth of a rectangle: 23 20 Area of the rectangle is : 460 Enter the base and height of the triangle: 2 5 Area of the triangle is : 5 </pre></\\'area></m<<></pre></a*b*c<<> C++ ירושה היררכית
ירושה היררכית מוגדרת כתהליך של גזירת יותר ממחלקה אחת ממחלקת בסיס.

תחביר של ירושה היררכית:
class A { // body of the class A. } class B : public A { // body of class B. } class C : public A { // body of class C. } class D : public A { // body of class D. } בואו נראה דוגמה פשוטה:
צומת רשימה ב-java
#include using namespace std; class Shape // Declaration of base class. { public: int a; int b; void get_data(int n,int m) { a= n; b = m; } }; class Rectangle : public Shape // inheriting Shape class { public: int rect_area() { int result = a*b; return result; } }; class Triangle : public Shape // inheriting Shape class { public: int triangle_area() { float result = 0.5*a*b; return result; } }; int main() { Rectangle r; Triangle t; int length,breadth,base,height; std::cout << 'Enter the length and breadth of a rectangle: ' <>length>>breadth; r.get_data(length,breadth); int m = r.rect_area(); std::cout << 'Area of the rectangle is : ' <<m<< std::endl; std::cout << \\'enter the base and height of triangle: \\' <>base>>height; t.get_data(base,height); float n = t.triangle_area(); std::cout <<\\'area of the triangle is : \\' << n<<std::endl; return 0; } < pre> <p>Output:</p> <pre> Enter the length and breadth of a rectangle: 23 20 Area of the rectangle is : 460 Enter the base and height of the triangle: 2 5 Area of the triangle is : 5 </pre></\\'area></m<<>