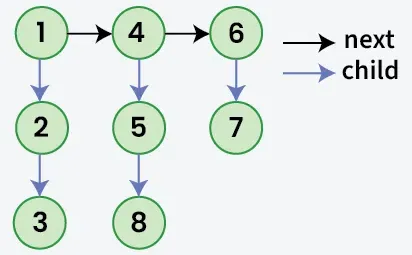
נתון רשימה מקושרת שבו בנוסף ל הַבָּא מצביע לכל צומת יש a יֶלֶד מצביע שעשוי להצביע על רשימה נפרדת או לא. ייתכן שיש לרשימות ילדים אלו אחד או יותר ילדים משלהם לייצר א רב רמות רשימה מקושרת. בהתחשב ב רֹאשׁ של רמה ראשונה של הרשימה. המשימה היא ל לְשַׁטֵחַ הרשימה כך שכל הצמתים יופיעו ב-a ברמה אחת רשימה מקושרת. שטחו את הרשימה בצורה שכל הצמתים ב- רמה ראשונה צריך לבוא רֵאשִׁית ואז צמתים של שְׁנִיָה רמה וכן הלאה.
דוגמאות:
קֶלֶט:
רשימת מערכי java ממוינת
רשימת ג'אווהתְפוּקָה: 1->4->6->2->5->7->3->8
הֶסבֵּר: הרשימה המקושרת הרב-שכבתית משוטחת מכיוון שאין לה מצביעי צאצא.
דנו השטחה של רשימה מקושרת מרובת רמות כאשר לצמתים יש שני מצביעים למטה והבא. בפוסט הקודם אנחנו שָׁטוּחַ הרשימה המקושרת ברמה ברמה. איך לשטח רשימה מקושרת כשאנחנו תמיד צריכים לעבד את מצביע למטה לפני הבא בכל צומת.
תוכן עניינים
[גישה צפויה] שימוש ברקורסיה - O(n) זמן ו-O(n) מרחב
C++הגישה היא ל באופן רקורסיבי לשטח א מקושר רב רמות רשימה על ידי חציית כל צומת וצמתי הצאצא שלו. רֵאשִׁית לשטח את רשימת הילדים באמצעות רקורסיה. לאחר שיטוח רשימת הילדים המשך ל- הצומת הבא ברצף. במהלך המעבר לשמור על א הַפנָיָה אל ה צומת שביקר בעבר ולקשר אותו לצומת הנוכחי. תהליך זה מבטיח שכל הצמתים מרמות שונות מחוברים ב-a רשימה ליניארית אחת תוך שמירה על סדר עומק.
ג'אווה סטטית
// A C++ program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise #include
// A Java program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise class Node { int data; Node next down; Node(int x) { data = x; next = down = null; } } class GfG { static void flattenList(Node curr Node[] prev) { if (curr == null) return; // Add the current element to the list. if (prev[0] != null) prev[0].next = curr; prev[0] = curr; // Store the next pointer Node next = curr.next; // Recursively add the bottom list flattenList(curr.down prev); // Recursively add the next list flattenList(next prev); } static void printList(Node head) { Node curr = head; while (curr != null) { System.out.print(curr.data + ' '); curr = curr.next; } System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node(5); head.down = new Node(7); head.down.down = new Node(8); head.down.down.down = new Node(30); head.next = new Node(10); head.next.next = new Node(19); head.next.next.down = new Node(22); head.next.next.down.down = new Node(50); head.next.next.next = new Node(28); Node[] prev = new Node[1]; flattenList(head prev); printList(head); } }
# A Python program to flatten a multi- # linked list depth-wise class Node: def __init__(self x): self.data = x self.next = None self.down = None def flatten_list(curr prev): if curr is None: return # Add the current element to the list. if prev[0] is not None: prev[0].next = curr prev[0] = curr # Store the next pointer next_node = curr.next # Recursively add the bottom list flatten_list(curr.down prev) # Recursively add the next list flatten_list(next_node prev) def print_list(head): curr = head while curr is not None: print(curr.data end=' ') curr = curr.next print() if __name__ == '__main__': # Create a hard coded multi-linked list. # 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 # | | # 7 22 # | | # 8 50 # | # 30 head = Node(5) head.down = Node(7) head.down.down = Node(8) head.down.down.down = Node(30) head.next = Node(10) head.next.next = Node(19) head.next.next.down = Node(22) head.next.next.down.down = Node(50) head.next.next.next = Node(28) prev = [None] flatten_list(head prev) print_list(head)
// A C# program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using System; class Node { public int data; public Node next down; public Node(int x) { data = x; next = down = null; } } class GfG { static void FlattenList(Node curr ref Node prev) { if (curr == null) return; // Add the current element to the list. if (prev != null) prev.next = curr; prev = curr; // Store the next pointer Node next = curr.next; // Recursively add the bottom list FlattenList(curr.down ref prev); // Recursively add the next list FlattenList(next ref prev); } static void PrintList(Node head) { Node curr = head; while (curr != null) { Console.Write(curr.data + ' '); curr = curr.next; } Console.WriteLine(); } static void Main(string[] args) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node(5); head.down = new Node(7); head.down.down = new Node(8); head.down.down.down = new Node(30); head.next = new Node(10); head.next.next = new Node(19); head.next.next.down = new Node(22); head.next.next.down.down = new Node(50); head.next.next.next = new Node(28); Node prev = null; FlattenList(head ref prev); PrintList(head); } }
// A Javascript program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.next = null; this.down = null; } } function flattenList(curr prev) { if (curr === null) return; // Add the current element to the list. if (prev[0] !== null) prev[0].next = curr; prev[0] = curr; // Store the next pointer let next = curr.next; // Recursively add the bottom list flattenList(curr.down prev); // Recursively add the next list flattenList(next prev); } function printList(head) { let curr = head; while (curr !== null) { console.log(curr.data); curr = curr.next; } } // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 let head = new Node(5); head.down = new Node(7); head.down.down = new Node(8); head.down.down.down = new Node(30); head.next = new Node(10); head.next.next = new Node(19); head.next.next.down = new Node(22); head.next.next.down.down = new Node(50); head.next.next.next = new Node(28); let prev = [null]; flattenList(head prev); printList(head);
תְפוּקָה
5 7 8 30 10 19 22 50 28
[גישה חלופית] שימוש במחסנית - O(n) זמן ו-O(n) Space
C++הגישה היא לחצות את רשימה מקושרת מרובת רמות באמצעות א לַעֲרוֹם . התחל ב דוחף את צומת ראש על הערימה. ואז בזמן שה המחסנית אינה ריקה פּוֹפּ הצומת העליון ולעבד אותו. עבור כל צומת לִדחוֹף שֶׁלָה מצביעי הבא ולמטה (אם הם קיימים) על הערימה. במהלך תהליך זה קשר את הצומת הנוכחי לצומת הקודם שמירה על הרשימה בצורה שטוחה. המעבר מבטיח שצמתים מכל הרמות מחוברים ב-a רשימה מקושרת ברמה אחת שמירה על סדר העומק.
// A C++ program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack #include
// A Java program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack import java.util.Stack; class Node { int data; Node next down; Node(int x) { data = x; next = down = null; } } class GfG { static void flattenList(Node head) { if (head == null) return; Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>(); stack.push(head); Node prev = null; while (!stack.isEmpty()) { Node curr = stack.pop(); // Push the next node first if (curr.next != null) stack.push(curr.next); // Push the bottom node into stack if (curr.down != null) stack.push(curr.down); // Add the current element to the list if (prev != null) prev.next = curr; prev = curr; } } static void printList(Node head) { Node curr = head; while (curr != null) { System.out.print(curr.data + ' '); curr = curr.next; } System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node(5); head.down = new Node(7); head.down.down = new Node(8); head.down.down.down = new Node(30); head.next = new Node(10); head.next.next = new Node(19); head.next.next.down = new Node(22); head.next.next.down.down = new Node(50); head.next.next.next = new Node(28); flattenList(head); printList(head); } }
# A Python program to flatten a multi- # linked list depth-wise using stack class Node: def __init__(self x): self.data = x self.next = None self.down = None def flatten_list(head): if head is None: return stack = [head] prev = None while stack: curr = stack.pop() # Push the next node first if curr.next: stack.append(curr.next) # Push the bottom node into stack if curr.down: stack.append(curr.down) # Add the current element to the list if prev: prev.next = curr prev = curr def print_list(head): curr = head while curr: print(curr.data end=' ') curr = curr.next print() if __name__ == '__main__': # Create a hard coded multi-linked list. # 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 # | | # 7 22 # | | # 8 50 # | # 30 head = Node(5) head.down = Node(7) head.down.down = Node(8) head.down.down.down = Node(30) head.next = Node(10) head.next.next = Node(19) head.next.next.down = Node(22) head.next.next.down.down = Node(50) head.next.next.next = Node(28) flatten_list(head) print_list(head)
// A C# program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Node { public int data; public Node next down; public Node(int x) { data = x; next = down = null; } } class GfG { static void FlattenList(Node head) { if (head == null) return; Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>(); stack.Push(head); Node prev = null; while (stack.Count > 0) { Node curr = stack.Pop(); // Push the next node first if (curr.next != null) stack.Push(curr.next); // Push the bottom node into stack if (curr.down != null) stack.Push(curr.down); // Add the current element to the list if (prev != null) prev.next = curr; prev = curr; } } static void PrintList(Node head) { Node curr = head; while (curr != null) { Console.Write(curr.data + ' '); curr = curr.next; } Console.WriteLine(); } static void Main(string[] args) { // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 Node head = new Node(5); head.down = new Node(7); head.down.down = new Node(8); head.down.down.down = new Node(30); head.next = new Node(10); head.next.next = new Node(19); head.next.next.down = new Node(22); head.next.next.down.down = new Node(50); head.next.next.next = new Node(28); FlattenList(head); PrintList(head); } }
// A Javascript program to flatten a multi- // linked list depth-wise using stack class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.next = null; this.down = null; } } function flattenList(head) { if (head === null) return; let stack = [head]; let prev = null; while (stack.length > 0) { let curr = stack.pop(); // Push the next node first if (curr.next !== null) stack.push(curr.next); // Push the bottom node into stack if (curr.down !== null) stack.push(curr.down); // Add the current element to the list if (prev !== null) prev.next = curr; prev = curr; } } function printList(head) { let curr = head; while (curr !== null) { console.log(curr.data); curr = curr.next; } } // Create a hard coded multi-linked list. // 5 -> 10 -> 19 -> 28 // | | // 7 22 // | | // 8 50 // | // 30 let head = new Node(5); head.down = new Node(7); head.down.down = new Node(8); head.down.down.down = new Node(30); head.next = new Node(10); head.next.next = new Node(19); head.next.next.down = new Node(22); head.next.next.down.down = new Node(50); head.next.next.next = new Node(28); flattenList(head); printList(head);
תְפוּקָה
5 7 8 30 10 19 22 50 28