בהינתן א גרף לא מכוון מחובר מיוצג על ידי רשימת סמיכות adjList[][] עִם נ צמתים ו מ קצוות כאשר לכל צומת יש a תווית מובהקת מִן 0 עד n-1 וכל adj[i] מייצג את רשימת הקודקודים המחוברים לקודקוד i.
צור א שיבוט של הגרף כאשר כל צומת בגרף מכיל מספר שלם val ומערך ( שכנים ) של צמתים המכילים צמתים הסמוכים לצומת הנוכחי.
פקודת arp
class Node {
val: מספר שלם
שכנים: רשימה[צומת]
}
המשימה שלך היא לשכפל את הגרף הנתון ולהחזיר הפניה לגרף המשובט.
פֶּתֶק: אם תחזיר עותק נכון של הגרף הנתון הפלט יהיה נכון; אחרת אם העותק שגוי הוא יודפס שקר.
דוגמאות
קֶלֶט: n = 4 adjList[][] = [[1 2] [0 2] [0 1 3] [2]]
תְפוּקָה: נָכוֹן
הֶסבֵּר:
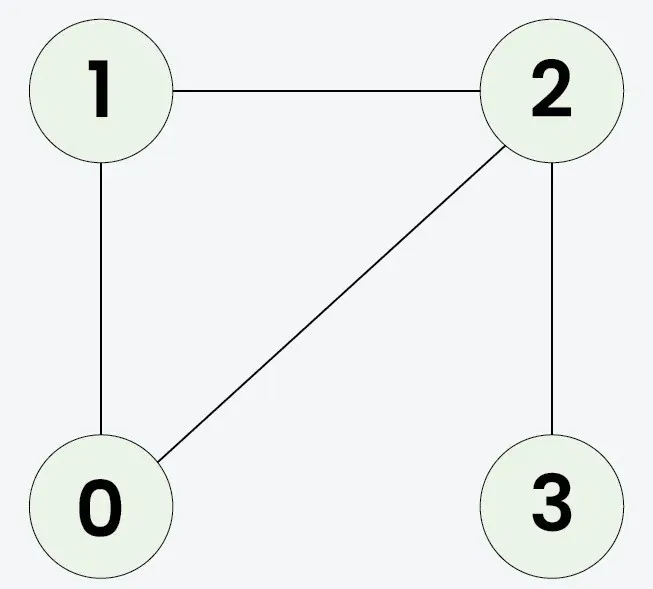
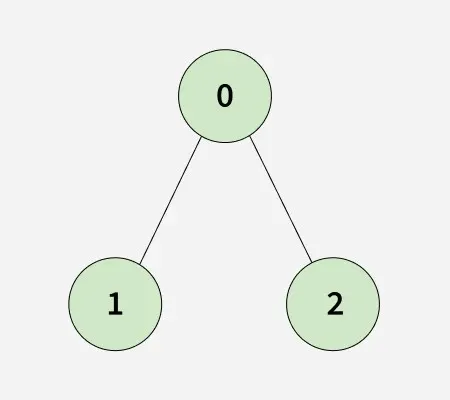
מכיוון שהגרף המשובט זהה למקור הפלט יהיה נכון.קֶלֶט: n = 3 adjList[][] = [[1 2] [0] [0]]
תְפוּקָה: נָכוֹן
הֶסבֵּר:
מכיוון שהגרף המשובט זהה למקור הפלט יהיה נכון.
תוכן עניינים
- למה אנחנו צריכים לעקוב אחר הצמתים שביקרו/משובטים?
- כיצד לעקוב אחר הצמתים שביקרו/משובטים?
- כיצד לחבר צמתים שיבוטים?
- כיצד לבדוק אם הגרף המשובט נכון?
- [גישה 1] שימוש בחציית BFS - O(V+E) זמן ומרחב O(V)
- [גישה 2] שימוש במעבר DFS - O(V+E) זמן ומרחב O(V)
למה אנחנו צריכים לעקוב אחר הצמתים שביקרו/משובטים?
עלינו לעקוב אחר צמתים שביקרו או משובטים כדי למנוע רקורסיה אינסופית ועבודה מיותרת בעת שיבוט גרף. מכיוון שגרפים יכולים להכיל מחזורים (שבהם צומת יכול להצביע חזרה לצומת שביקרתם בעבר) מבלי לעקוב אחר הצמתים שכבר שיבצנו, פונקציית השיבוט תבקר שוב ושוב באותם צמתים וכתוצאה מכך הצפה של מחסנית או שכפול שגוי.
כיצד לעקוב אחר הצמתים שביקרו/משובטים?
יש צורך ב-HashMap/Map על מנת לשמור על כל הצמתים שכבר נוצרו. חנויות מפתח : הפניה/כתובת של הצומת המקורי חנויות ערך : הפניה/כתובת של הצומת המשובט נוצר עותק של כל צמתי הגרף.
כיצד לחבר צמתים שיבוטים?
בעת ביקור בקודקודים השכנים של א צוֹמֶת ב קבל את המשובט המתאים צוֹמֶת בשבילך בוא נקרא לזה IN כעת בקר בכל הצמתים השכנים עבור ב ולכל שכן מצא את צומת השיבוט המתאים (אם לא נמצא צור אחד) ולאחר מכן לחץ לוקטור השכן של IN צוֹמֶת.
כיצד לבדוק אם הגרף המשובט נכון?
בצע חציית BFS על הגרף המקורי לפני השיבוט ואז שוב על הגרף המשובט לאחר השלמת השיבוט. במהלך כל מעבר הדפס את הערך של כל צומת יחד עם הכתובת שלו (או הפניה). כדי לאמת את נכונות השיבוט השווה את סדר הצמתים שבהם ביקרו בשני המעברים. אם ערכי הצומת מופיעים באותו סדר אבל הכתובות (או ההפניות) שלהם שונות, זה מאשר שהגרף שוכפל בהצלחה ובתקין.
מה זה f5 במקלדת
גלה כיצד לעשות זאת לשכפל גרף לא מכוון כולל גרפים עם מספר רכיבים מחוברים באמצעות BFS או DFS כדי להבטיח עותק עמוק שלם של כל הצמתים והקצוות.
[גישה 1] שימוש בחציית BFS - O(V+E) זמן ומרחב O(V)
C++בגישת BFS הגרף משובט באופן איטרטיבי באמצעות תור. אנו מתחילים בשיבוט הצומת הראשוני והצבתו בתור. כאשר אנו מעבדים כל צומת מהתור אנו מבקרים את שכניו. אם שכן לא שובט עדיין, אנו יוצרים שיבוט מאחסן אותו במפה ומעמידים אותו בתור לעיבוד מאוחר יותר. לאחר מכן נוסיף את השיבוט של השכן לרשימת השכנים של הצומת הנוכחי. תהליך זה נמשך רמה אחר רמה ומבטיח שכל הצמתים יבקרו בסדר רוחב ראשון. BFS שימושי במיוחד כדי למנוע רקורסיה עמוקה וטיפול בגרפים גדולים או רחבים ביעילות.
#include
import java.util.*; // Definition for a Node class Node { public int val; public ArrayList<Node> neighbors; public Node() { neighbors = new ArrayList<>(); } public Node(int val) { this.val = val; neighbors = new ArrayList<>(); } } public class GfG { // Clone the graph public static Node cloneGraph(Node node) { if (node == null) return null; Map<Node Node> mp = new HashMap<>(); Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>(); // Clone the starting node Node clone = new Node(node.val); mp.put(node clone); q.offer(node); while (!q.isEmpty()) { Node current = q.poll(); for (Node neighbor : current.neighbors) { // Clone neighbor if it hasn't been cloned yet if (!mp.containsKey(neighbor)) { mp.put(neighbor new Node(neighbor.val)); q.offer(neighbor); } // Add the clone of the neighbor to the current node's clone mp.get(current).neighbors.add(mp.get(neighbor)); } } return mp.get(node); } // Build graph public static Node buildGraph() { Node node1 = new Node(0); Node node2 = new Node(1); Node node3 = new Node(2); Node node4 = new Node(3); node1.neighbors.addAll(new ArrayList<> (Arrays.asList(node2 node3))); node2.neighbors.addAll(new ArrayList<> (Arrays.asList(node1 node3))); node3.neighbors.addAll(new ArrayList<> (Arrays.asList(node1 node2 node4))); node4.neighbors.addAll(new ArrayList<> (Arrays.asList(node3))); return node1; } // Compare two graphs for structure and value public static boolean compareGraphs(Node n1 Node n2 HashMap<Node Node> visited) { if (n1 == null || n2 == null) return n1 == n2; if (n1.val != n2.val || n1 == n2) return false; visited.put(n1 n2); if (n1.neighbors.size() != n2.neighbors.size()) return false; for (int i = 0; i < n1.neighbors.size(); i++) { Node neighbor1 = n1.neighbors.get(i); Node neighbor2 = n2.neighbors.get(i); if (visited.containsKey(neighbor1)) { if (visited.get(neighbor1) != neighbor2) return false; } else { if (!compareGraphs(neighbor1 neighbor2 visited)) return false; } } return true; } public static void main(String[] args) { Node original = buildGraph(); Node cloned = cloneGraph(original); boolean isEqual = compareGraphs(original cloned new HashMap<>()); System.out.println(isEqual ? 'true' : 'false'); } }
from collections import deque # Definition for a Node class Node: def __init__(self val=0): self.val = val self.neighbors = [] # Clone the graph def cloneGraph(node): if not node: return None # Map to hold original nodes as keys and their clones as values mp = {} # Initialize BFS queue q = deque([node]) # Clone the starting node mp[node] = Node(node.val) while q: current = q.popleft() for neighbor in current.neighbors: # If neighbor not cloned yet if neighbor not in mp: mp[neighbor] = Node(neighbor.val) q.append(neighbor) # Link clone of neighbor to the clone of the current node mp[current].neighbors.append(mp[neighbor]) return mp[node] # Build graph def buildGraph(): node1 = Node(0) node2 = Node(1) node3 = Node(2) node4 = Node(3) node1.neighbors = [node2 node3] node2.neighbors = [node1 node3] node3.neighbors = [node1 node2 node4] node4.neighbors = [node3] return node1 # Compare two graphs structurally and by values def compareGraphs(n1 n2 visited): if not n1 or not n2: return n1 == n2 if n1.val != n2.val or n1 is n2: return False visited[n1] = n2 if len(n1.neighbors) != len(n2.neighbors): return False for i in range(len(n1.neighbors)): neighbor1 = n1.neighbors[i] neighbor2 = n2.neighbors[i] if neighbor1 in visited: if visited[neighbor1] != neighbor2: return False else: if not compareGraphs(neighbor1 neighbor2 visited): return False return True # Driver if __name__ == '__main__': original = buildGraph() cloned = cloneGraph(original) result = compareGraphs(original cloned {}) print('true' if result else 'false')
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; // Definition for a Node public class Node { public int val; public List<Node> neighbors; public Node() { neighbors = new List<Node>(); } public Node(int val) { this.val = val; neighbors = new List<Node>(); } } class GfG { // Clone the graph public static Node CloneGraph(Node node) { if (node == null) return null; var mp = new Dictionary<Node Node>(); var q = new Queue<Node>(); // Clone the starting node var clone = new Node(node.val); mp[node] = clone; q.Enqueue(node); while (q.Count > 0) { var current = q.Dequeue(); foreach (var neighbor in current.neighbors) { // If neighbor not cloned clone it and enqueue if (!mp.ContainsKey(neighbor)) { mp[neighbor] = new Node(neighbor.val); q.Enqueue(neighbor); } // Add clone of neighbor to clone of current mp[current].neighbors.Add(mp[neighbor]); } } return mp[node]; } // Build graph public static Node BuildGraph() { var node1 = new Node(0); var node2 = new Node(1); var node3 = new Node(2); var node4 = new Node(3); node1.neighbors.AddRange(new[] { node2 node3 }); node2.neighbors.AddRange(new[] { node1 node3 }); node3.neighbors.AddRange(new[] { node1 node2 node4 }); node4.neighbors.AddRange(new[] { node3 }); return node1; } // Compare two graphs for structure and value public static bool CompareGraphs(Node n1 Node n2 Dictionary<Node Node> visited) { if (n1 == null || n2 == null) return n1 == n2; if (n1.val != n2.val || ReferenceEquals(n1 n2)) return false; visited[n1] = n2; if (n1.neighbors.Count != n2.neighbors.Count) return false; for (int i = 0; i < n1.neighbors.Count; i++) { var neighbor1 = n1.neighbors[i]; var neighbor2 = n2.neighbors[i]; if (visited.ContainsKey(neighbor1)) { if (!ReferenceEquals(visited[neighbor1] neighbor2)) return false; } else { if (!CompareGraphs(neighbor1 neighbor2 visited)) return false; } } return true; } public static void Main() { var original = BuildGraph(); var cloned = CloneGraph(original); var visited = new Dictionary<Node Node>(); Console.WriteLine(CompareGraphs(original cloned visited) ? 'true' : 'false'); } }
// Definition for a Node class Node { constructor(val = 0) { this.val = val; this.neighbors = []; } } // Clone the graph function cloneGraph(node) { if (!node) return null; const mp = new Map(); const q = [node]; // Clone the initial node mp.set(node new Node(node.val)); while (q.length > 0) { const current = q.shift(); for (const neighbor of current.neighbors) { if (!mp.has(neighbor)) { mp.set(neighbor new Node(neighbor.val)); q.push(neighbor); } // Link clone of neighbor to clone of current mp.get(current).neighbors.push(mp.get(neighbor)); } } return mp.get(node); } // Build graph function buildGraph() { const node1 = new Node(0); const node2 = new Node(1); const node3 = new Node(2); const node4 = new Node(3); node1.neighbors = [node2 node3]; node2.neighbors = [node1 node3]; node3.neighbors = [node1 node2 node4]; node4.neighbors = [node3]; return node1; } // Compare two graphs structurally and by value function compareGraphs(n1 n2 visited = new Map()) { if (!n1 || !n2) return n1 === n2; if (n1.val !== n2.val || n1 === n2) return false; visited.set(n1 n2); if (n1.neighbors.length !== n2.neighbors.length) return false; for (let i = 0; i < n1.neighbors.length; i++) { const neighbor1 = n1.neighbors[i]; const neighbor2 = n2.neighbors[i]; if (visited.has(neighbor1)) { if (visited.get(neighbor1) !== neighbor2) return false; } else { if (!compareGraphs(neighbor1 neighbor2 visited)) return false; } } return true; } // Driver const original = buildGraph(); const cloned = cloneGraph(original); const result = compareGraphs(original cloned); console.log(result ? 'true' : 'false');
תְפוּקָה
true
[גישה 2] שימוש במעבר DFS - O(V+E) זמן ומרחב O(V)
C++בגישת DFS הגרף משובט באמצעות רקורסיה. אנו מתחילים מהצומת הנתון וחוקרים ככל האפשר לאורך כל ענף לפני החזרה לאחור. מפה (או מילון) משמשת כדי לעקוב אחר צמתים שכבר משובטים כדי להימנע מעיבוד אותו צומת מספר פעמים וכדי לטפל במחזורים. כאשר אנו נתקלים בצומת בפעם הראשונה אנו יוצרים שיבוט שלו ומאחסנים אותו במפה. לאחר מכן, עבור כל שכן של אותו צומת אנו משכפלים אותו באופן רקורסיבי ומוסיפים את השכן המשובט לשיבוט של הצומת הנוכחי. זה מבטיח שכל הצמתים יעברו ביקור עמוק לפני החזרה ומבנה הגרף מועתק נאמנה.
#include
import java.util.*; // Definition for a Node class Node { int val; ArrayList<Node> neighbors; Node() { neighbors = new ArrayList<>(); } Node(int val) { this.val = val; neighbors = new ArrayList<>(); } } public class GfG { // Map to hold original node to its copy static HashMap<Node Node> copies = new HashMap<>(); // Function to clone the graph using DFS public static Node cloneGraph(Node node) { // If the node is NULL return NULL if (node == null) return null; // If node is not yet cloned clone it if (!copies.containsKey(node)) { Node clone = new Node(node.val); copies.put(node clone); // Recursively clone neighbors for (Node neighbor : node.neighbors) { clone.neighbors.add(cloneGraph(neighbor)); } } // Return the clone return copies.get(node); } // Build graph public static Node buildGraph() { Node node1 = new Node(0); Node node2 = new Node(1); Node node3 = new Node(2); Node node4 = new Node(3); node1.neighbors.addAll(Arrays.asList(node2 node3)); node2.neighbors.addAll(Arrays.asList(node1 node3)); node3.neighbors.addAll(Arrays.asList(node1node2 node4)); node4.neighbors.addAll(Arrays.asList(node3)); return node1; } // Compare two graphs for structural and value equality public static boolean compareGraphs(Node node1 Node node2 HashMap<Node Node> visited) { if (node1 == null || node2 == null) return node1 == node2; if (node1.val != node2.val || node1 == node2) return false; visited.put(node1 node2); if (node1.neighbors.size() != node2.neighbors.size()) return false; for (int i = 0; i < node1.neighbors.size(); i++) { Node n1 = node1.neighbors.get(i); Node n2 = node2.neighbors.get(i); if (visited.containsKey(n1)) { if (visited.get(n1) != n2) return false; } else { if (!compareGraphs(n1 n2 visited)) return false; } } return true; } // Driver Code public static void main(String[] args) { Node original = buildGraph(); // Clone the graph Node cloned = cloneGraph(original); // Compare original and cloned graph boolean result = compareGraphs(original cloned new HashMap<>()); System.out.println(result ? 'true' : 'false'); } }
# Definition for a Node class Node: def __init__(self val=0 neighbors=None): self.val = val self.neighbors = neighbors if neighbors is not None else [] # Map to hold original node to its copy copies = {} # Function to clone the graph def cloneGraph(node): # If the node is None return None if not node: return None # If node is not yet cloned clone it if node not in copies: # Create a clone of the node clone = Node(node.val) copies[node] = clone # Recursively clone neighbors for neighbor in node.neighbors: clone.neighbors.append(cloneGraph(neighbor)) # Return the clone return copies[node] def buildGraph(): node1 = Node(0) node2 = Node(1) node3 = Node(2) node4 = Node(3) node1.neighbors = [node2 node3] node2.neighbors = [node1 node3] node3.neighbors = [node1 node2 node4] node4.neighbors = [node3] return node1 # Compare two graphs for structural and value equality def compareGraphs(node1 node2 visited): if not node1 or not node2: return node1 == node2 if node1.val != node2.val or node1 is node2: return False visited[node1] = node2 if len(node1.neighbors) != len(node2.neighbors): return False for i in range(len(node1.neighbors)): n1 = node1.neighbors[i] n2 = node2.neighbors[i] if n1 in visited: if visited[n1] != n2: return False else: if not compareGraphs(n1 n2 visited): return False return True # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': original = buildGraph() # Clone the graph using DFS cloned = cloneGraph(original) # Compare original and cloned graph visited = {} print('true' if compareGraphs(original cloned visited) else 'false')
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; public class Node { public int val; public List<Node> neighbors; public Node() { val = 0; neighbors = new List<Node>(); } public Node(int _val) { val = _val; neighbors = new List<Node>(); } } class GfG { // Dictionary to hold original node to its copy static Dictionary<Node Node> copies = new Dictionary<Node Node>(); // Function to clone the graph using DFS public static Node CloneGraph(Node node) { // If the node is NULL return NULL if (node == null) return null; // If node is not yet cloned clone it if (!copies.ContainsKey(node)) { Node clone = new Node(node.val); copies[node] = clone; // Recursively clone neighbors foreach (Node neighbor in node.neighbors) { clone.neighbors.Add(CloneGraph(neighbor)); } } // Return the clone return copies[node]; } // Build graph public static Node BuildGraph() { Node node1 = new Node(0); Node node2 = new Node(1); Node node3 = new Node(2); Node node4 = new Node(3); node1.neighbors.Add(node2); node1.neighbors.Add(node3); node2.neighbors.Add(node1); node2.neighbors.Add(node3); node3.neighbors.Add(node1); node3.neighbors.Add(node2); node3.neighbors.Add(node4); node4.neighbors.Add(node3); return node1; } // Compare two graphs for structural and value equality public static bool CompareGraphs(Node node1 Node node2 Dictionary<Node Node> visited) { if (node1 == null || node2 == null) return node1 == node2; if (node1.val != node2.val || node1 == node2) return false; visited[node1] = node2; if (node1.neighbors.Count != node2.neighbors.Count) return false; for (int i = 0; i < node1.neighbors.Count; i++) { Node n1 = node1.neighbors[i]; Node n2 = node2.neighbors[i]; if (visited.ContainsKey(n1)) { if (visited[n1] != n2) return false; } else { if (!CompareGraphs(n1 n2 visited)) return false; } } return true; } // Driver Code public static void Main() { Node original = BuildGraph(); // Clone the graph using DFS Node cloned = CloneGraph(original); // Compare original and cloned graph bool isEqual = CompareGraphs(original cloned new Dictionary<Node Node>()); Console.WriteLine(isEqual ? 'true' : 'false'); } }
// Definition for a Node class Node { constructor(val = 0) { this.val = val; this.neighbors = []; } } // Map to hold original node to its copy const copies = new Map(); // Function to clone the graph using DFS function cloneGraph(node) { // If the node is NULL return NULL if (node === null) return null; // If node is not yet cloned clone it if (!copies.has(node)) { const clone = new Node(node.val); copies.set(node clone); // Recursively clone neighbors for (let neighbor of node.neighbors) { clone.neighbors.push(cloneGraph(neighbor)); } } // Return the clone return copies.get(node); } // Build graph function buildGraph() { const node1 = new Node(0); const node2 = new Node(1); const node3 = new Node(2); const node4 = new Node(3); node1.neighbors.push(node2 node3); node2.neighbors.push(node1 node3); node3.neighbors.push(node1 node2 node4); node4.neighbors.push(node3); return node1; } // Compare two graphs for structural and value equality function compareGraphs(node1 node2 visited = new Map()) { if (!node1 || !node2) return node1 === node2; if (node1.val !== node2.val || node1 === node2) return false; visited.set(node1 node2); if (node1.neighbors.length !== node2.neighbors.length) return false; for (let i = 0; i < node1.neighbors.length; i++) { const n1 = node1.neighbors[i]; const n2 = node2.neighbors[i]; if (visited.has(n1)) { if (visited.get(n1) !== n2) return false; } else { if (!compareGraphs(n1 n2 visited)) return false; } } return true; } // Driver Code const original = buildGraph(); // Clone the graph using DFS const cloned = cloneGraph(original); // Compare original and cloned graph console.log(compareGraphs(original cloned) ? 'true' : 'false');
תְפוּקָה
true