מאמר זה ילמד אותך על סקירה מלאה של השימוש בלולאת WHILE ב-SQL Server. א לולאת WHILE היא הצהרת זרימת בקרה המשמשת לביצוע שוב ושוב את קבוצת ההצהרות עד לסיפוק התנאי שצוין . לולאה זו מתחילה בתנאי נתון, הערך אותו, ואם הוא TRUE, ההצהרות ייכנסו לתוך הלולאה לביצוע נוסף. אם התנאי יהפוך ל-FALSE, הוא לא יפעל. זה מרמז שלולאת ה-while ב-SQL Server יכולה לפעול אפס פעמים או יותר.
תרשים זרימה של WHILE Loop
תרשים הזרימה הבא יסביר את זרימת העבודה המלאה של לולאת WHILE בתוך SQL Server:
חציית עץ בינארי בהזמנה בדואר
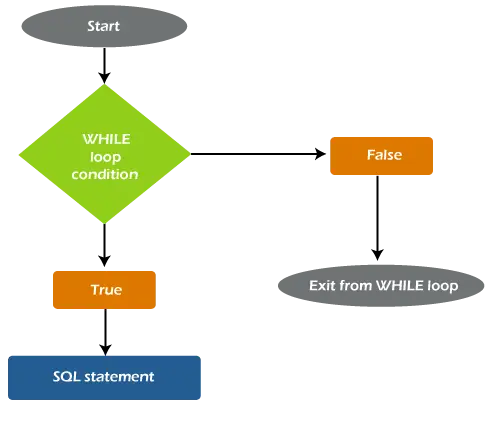
אנו יכולים לראות בתרשים זה שהמצב שצוין נבדק עבור כל איטרציה, ובהתבסס על תוצאת ההערכה, זרימת הקוד נקבעת. אם התוצאה מוערכת TRUE, זרימת הבקרה נכנסת לתוך הלולאה לביצוע נוסף. אם התוצאה המוערכת היא FALSE, זרימת הבקרה תצא מהלולאה, וכל הצהרה או שאילתה מחוץ ללולאה תבוצע.
תחביר
התחביר הבא ממחיש את לולאת WHILE ב-SQL Server:
WHILE boolean_condition BEGIN BREAK END;
בתחביר זה, יש לנו את הפרמטרים או הארגומנטים הבאים:
דוגמה ללולאה WHILE
תן לנו להבין כיצד לולאת WHILE עובדת ב-SQL Server באמצעות דוגמה. בדוגמה הנתונה, תחילה הכרזנו על ערך של סוג מספר שלם והגדר את הערך שלו ל-1. לאחר מכן, לולאת WHILE בודקת את התנאי, ואם כן נָכוֹן , הצהרת ההדפסה תודפס. כאשר הלולאה הופכת שֶׁקֶר , ההצהרה הבאה אחרי לולאת WHILE תודפס.
DECLARE @stud_value INT; SET @stud_value = 1; WHILE @stud_value <= 5 begin print 'mark henry'; set @stud_value="@stud_value" + 1; end; 'rose bennet'; < pre> <p>Executing this statement will return the following output:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/sql-server-tutorials/44/sql-server-while-loop-2.webp" alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <p>In the above WHILE loop code snippet, we must increment the variable's value after each iteration. See the below part of the above code line as <strong>SET @stud_value = @stud_value + 1</strong> . If we do not write this statement, the loop will execute infinitely because it cannot becomes FALSE.</p> <pre> BEGIN PRINT 'Mark Henry'; SET @stud_value = @stud_value + 1; END; </pre> <h3>Infinite WHILE Loop</h3> <p>An infinite loop occurs when the evaluation of a condition will never be false. Therefore, the loop will never end and be executed forever. The loop in the following code snippet is infinite because the variable's value is not incremented.</p> <pre> DECLARE @stud_value INT; SET @stud_value = 1; WHILE @stud_value <= 5 begin print 'please stop execution!' end; < pre> <p>Executing the loop will display the below output. This loop will never end its execution until we do not cancel their execution of the query manually.</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/sql-server-tutorials/44/sql-server-while-loop-3.webp" alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <h3>Inserting Records with WHILE Loop</h3> <p>We can also use the WHILE loop to insert records into the defined table. Let us see how to inserts dummy records into the database. First, we will create a table named <strong>'bikeshop'</strong> containing three columns: <strong>Id, bike_name,</strong> and <strong>price</strong> . Execute the following statement to create this table:</p> <pre> CREATE TABLE bikeshop ( Id INT PRIMARY KEY IDENTITY, bike_name VARCHAR (50) NOT NULL, price FLOAT ) </pre> <p>Next, we will use the WHILE loop to insert ten records into this table by executing the following script:</p> <pre> DECLARE @count INT; SET @count = 1; WHILE @count <= 10 begin insert into bikeshop values('bike-' + cast(@count as varchar), @count*5000) set @count="@count" 1; end; < pre> <p>In this code, we have declared a variable @ <strong>count</strong> and then initialize its value with 1 using a SET clause. Next, we have to define the loop body that executes the INSERT statement to add one record in each execution. The <strong>bike_name column</strong> will append the value of a @count variable with the string <strong>Bike</strong> , and the <strong>price</strong> column determines by the value of a @count variable multiplied by <strong>5000</strong> . The loop will execute until the value of the @count variable becomes FALSE. It means the WHILE loop will execute ten times and <strong>inserts ten records</strong> into the table bikeshop.</p> <p>Now, we can verify all the records of the bikeshop table with the SELECT statement. It will display the following output:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/sql-server-tutorials/44/sql-server-while-loop-4.webp" alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <h3>BREAK Statement</h3> <p>SQL Server also allows us to use the BREAK statement in the WHILE loop like programming languages. This statement is used to <strong>immediately stop the current iteration of the loop</strong> , and control flow resumes with the next statement after the loop. In general, we will use the <a href="/sql-server-if-else"> <strong>IF...ELSE statement</strong> </a> to check whether or not a condition has occurred.</p> <p>The following example will explain how to use the BREAK statement in the WHILE loop:</p> <pre> DECLARE @count INT; SET @count = 1; WHILE @count = 6 BEGIN BREAK END SET @Count = @Count + 1 END; </pre> <p>Executing the code will display the below output:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/sql-server-tutorials/44/sql-server-while-loop-5.webp" alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <p>The value of the variable is first evaluated in this code. If it is TRUE, the control enters into the loop and prints the statement. When the variable value is greater than or equal to 6, control enters the IF...ELSE block and executes the BREAK statement to terminate the loop. If an IF...ELSE block fails to meet the condition; then, the loop will keep running until the condition is changed to FALSE.</p> <h3>CONTINUE Statement</h3> <p>SQL Server also allows us to use the CONTINUE statement in the WHILE loop like programming languages. This statement immediately <strong>terminates the current execution of the loop when the specified condition is met</strong> , and control flow returns to the beginning of the loop. In general, the IF...ELSE statement will be used to test whether or not a condition has been met.</p> <p>The CONTINUE statement in the WHILE loop is demonstrated in the following example. In this example, we'll assume that we wish to use a WHILE loop to <strong>print only odd values</strong> . The CONTINUE statement can be used to do this. This example will first <strong>test</strong> whether the variable value is <strong>odd or even</strong> . If it is even, the execution goes inside the IF…ELSE statement blocks and decrement the variable value by one. Then, it will execute the CONTINUE statement and starts a new iteration from the beginning.</p> <pre> DECLARE @Count INT SET @Count = 1 WHILE (@Count <= 1 2="0" 44 20) begin if @count % set + continue end print 'the odd value is=" + CONVERT(VARCHAR, @Count) SET @Count = @Count + 1 END </pre> <p>Executing the code snippet will display the below output:</p> <img src=" techcodeview.com img sql-server-tutorials sql-server-while-loop-6.webp' alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <h3>How to implementing paging with WHILE loop in SQL Server?</h3> <p>We can also use the WHILE loop for implementing the paging. Paging allows displaying the subset of records from a table at any particular time. The following example will explain this concept. The WHILE loop in the code will select two records from the bikeshop table at a time. The records that have been chosen are then displayed in the output.</p> <pre> DECLARE @count INT DECLARE @limit INT; SET @count = 0 SET @limit = 2; WHILE @count <10 begin select * from bikeshop order by id offset @count rows fetch next @limit only set + 2; end; < pre> <p>Executing the code snippet will return the below output:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/sql-server-tutorials/44/sql-server-while-loop-7.webp" alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <h3>Nested WHILE Loop</h3> <p>The Nested WHILE Loop in SQL Server is simply a WHILE Loop written inside another WHILE Loop. When we work on multi-layered data, the Nested WHILE loops are essential. Because this concept is useful in extracting the layered data when we want to select them, it is recommended to be careful while using the nested loop.</p> <p> <strong>Syntax</strong> </p> <p>The following syntax illustrate the working of the nested WHILE Loop in SQL Server:</p> <pre> WHILE Expression BEGIN WHILE @Val2 <= 10 begin --second while loop statements sql end --this statement is outside the second --which first -- this < pre> <p>Let us explain this syntax step by step:</p> <p> <strong>Step 1:</strong> The loop starts by checking the first WHILE loop condition, and if it finds a false result, it will exit from While Loop. Otherwise, if the result is true, the control goes inside the BEGIN and END block for further execution. This block will start the execution of the second WHILE loop. See step 2.</p> <p> <strong>Step 2:</strong> This step will check the condition in the Nested WHILE Loop, and if it is false, the second loop will be exit and execute the statement outside this. Otherwise, if the result is true, the control goes inside the BEGIN and END block for further execution.</p> <p> <strong>Step 3:</strong> Once all the statements execute from the second WHILE loop, the control goes to the first WHILE and repeats the first step.</p> <p> <strong>Example</strong> </p> <p>The following example will print the multiplication table of 5 up to 10 using the nested WHILE loop.</p> <pre> DECLARE @val1 INT DECLARE @val2 INT SET @val1 = 5 SET @val2 = 1 WHILE @val1 <= 5 44 begin while @val2 <="10" print convert(varchar, @val1) + ' * @val2) techcodeview.com img sql-server-tutorials sql-server-while-loop-8.webp' alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <h2>Conclusion</h2> <p>The WHILE loop is a useful method when there is a need to execute a SQL script repeatedly. The article explained how to work with the WHILE loop in MS SQL Server to execute operations such as record insertion and pagination with a simple example. Here we have also learned the BREAK and CONTINUE statements to control the WHILE loop iteration.</p> <hr></=></pre></=></pre></10></pre></=></pre></=></pre></=></pre></=> לולאת WHILE אינסופית
לולאה אינסופית מתרחשת כאשר ההערכה של תנאי לעולם לא תהיה שקרית. לכן, הלולאה לעולם לא תיגמר ותצא להורג לנצח. הלולאה בקטע הקוד הבא היא אינסופית מכיוון שערכו של המשתנה אינו מוגדל.
DECLARE @stud_value INT; SET @stud_value = 1; WHILE @stud_value <= 5 begin print \'please stop execution!\' end; < pre> <p>Executing the loop will display the below output. This loop will never end its execution until we do not cancel their execution of the query manually.</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/sql-server-tutorials/44/sql-server-while-loop-3.webp" alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <h3>Inserting Records with WHILE Loop</h3> <p>We can also use the WHILE loop to insert records into the defined table. Let us see how to inserts dummy records into the database. First, we will create a table named <strong>'bikeshop'</strong> containing three columns: <strong>Id, bike_name,</strong> and <strong>price</strong> . Execute the following statement to create this table:</p> <pre> CREATE TABLE bikeshop ( Id INT PRIMARY KEY IDENTITY, bike_name VARCHAR (50) NOT NULL, price FLOAT ) </pre> <p>Next, we will use the WHILE loop to insert ten records into this table by executing the following script:</p> <pre> DECLARE @count INT; SET @count = 1; WHILE @count <= 10 begin insert into bikeshop values(\'bike-\' + cast(@count as varchar), @count*5000) set @count="@count" 1; end; < pre> <p>In this code, we have declared a variable @ <strong>count</strong> and then initialize its value with 1 using a SET clause. Next, we have to define the loop body that executes the INSERT statement to add one record in each execution. The <strong>bike_name column</strong> will append the value of a @count variable with the string <strong>Bike</strong> , and the <strong>price</strong> column determines by the value of a @count variable multiplied by <strong>5000</strong> . The loop will execute until the value of the @count variable becomes FALSE. It means the WHILE loop will execute ten times and <strong>inserts ten records</strong> into the table bikeshop.</p> <p>Now, we can verify all the records of the bikeshop table with the SELECT statement. It will display the following output:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/sql-server-tutorials/44/sql-server-while-loop-4.webp" alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <h3>BREAK Statement</h3> <p>SQL Server also allows us to use the BREAK statement in the WHILE loop like programming languages. This statement is used to <strong>immediately stop the current iteration of the loop</strong> , and control flow resumes with the next statement after the loop. In general, we will use the <a href="/sql-server-if-else"> <strong>IF...ELSE statement</strong> </a> to check whether or not a condition has occurred.</p> <p>The following example will explain how to use the BREAK statement in the WHILE loop:</p> <pre> DECLARE @count INT; SET @count = 1; WHILE @count = 6 BEGIN BREAK END SET @Count = @Count + 1 END; </pre> <p>Executing the code will display the below output:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/sql-server-tutorials/44/sql-server-while-loop-5.webp" alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <p>The value of the variable is first evaluated in this code. If it is TRUE, the control enters into the loop and prints the statement. When the variable value is greater than or equal to 6, control enters the IF...ELSE block and executes the BREAK statement to terminate the loop. If an IF...ELSE block fails to meet the condition; then, the loop will keep running until the condition is changed to FALSE.</p> <h3>CONTINUE Statement</h3> <p>SQL Server also allows us to use the CONTINUE statement in the WHILE loop like programming languages. This statement immediately <strong>terminates the current execution of the loop when the specified condition is met</strong> , and control flow returns to the beginning of the loop. In general, the IF...ELSE statement will be used to test whether or not a condition has been met.</p> <p>The CONTINUE statement in the WHILE loop is demonstrated in the following example. In this example, we'll assume that we wish to use a WHILE loop to <strong>print only odd values</strong> . The CONTINUE statement can be used to do this. This example will first <strong>test</strong> whether the variable value is <strong>odd or even</strong> . If it is even, the execution goes inside the IF…ELSE statement blocks and decrement the variable value by one. Then, it will execute the CONTINUE statement and starts a new iteration from the beginning.</p> <pre> DECLARE @Count INT SET @Count = 1 WHILE (@Count <= 1 2="0" 44 20) begin if @count % set + continue end print \'the odd value is=" + CONVERT(VARCHAR, @Count) SET @Count = @Count + 1 END </pre> <p>Executing the code snippet will display the below output:</p> <img src=" techcodeview.com img sql-server-tutorials sql-server-while-loop-6.webp\' alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <h3>How to implementing paging with WHILE loop in SQL Server?</h3> <p>We can also use the WHILE loop for implementing the paging. Paging allows displaying the subset of records from a table at any particular time. The following example will explain this concept. The WHILE loop in the code will select two records from the bikeshop table at a time. The records that have been chosen are then displayed in the output.</p> <pre> DECLARE @count INT DECLARE @limit INT; SET @count = 0 SET @limit = 2; WHILE @count <10 begin select * from bikeshop order by id offset @count rows fetch next @limit only set + 2; end; < pre> <p>Executing the code snippet will return the below output:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/sql-server-tutorials/44/sql-server-while-loop-7.webp" alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <h3>Nested WHILE Loop</h3> <p>The Nested WHILE Loop in SQL Server is simply a WHILE Loop written inside another WHILE Loop. When we work on multi-layered data, the Nested WHILE loops are essential. Because this concept is useful in extracting the layered data when we want to select them, it is recommended to be careful while using the nested loop.</p> <p> <strong>Syntax</strong> </p> <p>The following syntax illustrate the working of the nested WHILE Loop in SQL Server:</p> <pre> WHILE Expression BEGIN WHILE @Val2 <= 10 begin --second while loop statements sql end --this statement is outside the second --which first -- this < pre> <p>Let us explain this syntax step by step:</p> <p> <strong>Step 1:</strong> The loop starts by checking the first WHILE loop condition, and if it finds a false result, it will exit from While Loop. Otherwise, if the result is true, the control goes inside the BEGIN and END block for further execution. This block will start the execution of the second WHILE loop. See step 2.</p> <p> <strong>Step 2:</strong> This step will check the condition in the Nested WHILE Loop, and if it is false, the second loop will be exit and execute the statement outside this. Otherwise, if the result is true, the control goes inside the BEGIN and END block for further execution.</p> <p> <strong>Step 3:</strong> Once all the statements execute from the second WHILE loop, the control goes to the first WHILE and repeats the first step.</p> <p> <strong>Example</strong> </p> <p>The following example will print the multiplication table of 5 up to 10 using the nested WHILE loop.</p> <pre> DECLARE @val1 INT DECLARE @val2 INT SET @val1 = 5 SET @val2 = 1 WHILE @val1 <= 5 44 begin while @val2 <="10" print convert(varchar, @val1) + \' * @val2) techcodeview.com img sql-server-tutorials sql-server-while-loop-8.webp\' alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <h2>Conclusion</h2> <p>The WHILE loop is a useful method when there is a need to execute a SQL script repeatedly. The article explained how to work with the WHILE loop in MS SQL Server to execute operations such as record insertion and pagination with a simple example. Here we have also learned the BREAK and CONTINUE statements to control the WHILE loop iteration.</p> <hr></=></pre></=></pre></10></pre></=></pre></=></pre></=>
לאחר מכן, נשתמש בלולאת WHILE כדי להוסיף עשר רשומות לטבלה זו על ידי ביצוע הסקריפט הבא:
רשימת מערך ממוינת
DECLARE @count INT; SET @count = 1; WHILE @count <= 10 begin insert into bikeshop values(\'bike-\' + cast(@count as varchar), @count*5000) set @count="@count" 1; end; < pre> <p>In this code, we have declared a variable @ <strong>count</strong> and then initialize its value with 1 using a SET clause. Next, we have to define the loop body that executes the INSERT statement to add one record in each execution. The <strong>bike_name column</strong> will append the value of a @count variable with the string <strong>Bike</strong> , and the <strong>price</strong> column determines by the value of a @count variable multiplied by <strong>5000</strong> . The loop will execute until the value of the @count variable becomes FALSE. It means the WHILE loop will execute ten times and <strong>inserts ten records</strong> into the table bikeshop.</p> <p>Now, we can verify all the records of the bikeshop table with the SELECT statement. It will display the following output:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/sql-server-tutorials/44/sql-server-while-loop-4.webp" alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <h3>BREAK Statement</h3> <p>SQL Server also allows us to use the BREAK statement in the WHILE loop like programming languages. This statement is used to <strong>immediately stop the current iteration of the loop</strong> , and control flow resumes with the next statement after the loop. In general, we will use the <a href="/sql-server-if-else"> <strong>IF...ELSE statement</strong> </a> to check whether or not a condition has occurred.</p> <p>The following example will explain how to use the BREAK statement in the WHILE loop:</p> <pre> DECLARE @count INT; SET @count = 1; WHILE @count = 6 BEGIN BREAK END SET @Count = @Count + 1 END; </pre> <p>Executing the code will display the below output:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/sql-server-tutorials/44/sql-server-while-loop-5.webp" alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <p>The value of the variable is first evaluated in this code. If it is TRUE, the control enters into the loop and prints the statement. When the variable value is greater than or equal to 6, control enters the IF...ELSE block and executes the BREAK statement to terminate the loop. If an IF...ELSE block fails to meet the condition; then, the loop will keep running until the condition is changed to FALSE.</p> <h3>CONTINUE Statement</h3> <p>SQL Server also allows us to use the CONTINUE statement in the WHILE loop like programming languages. This statement immediately <strong>terminates the current execution of the loop when the specified condition is met</strong> , and control flow returns to the beginning of the loop. In general, the IF...ELSE statement will be used to test whether or not a condition has been met.</p> <p>The CONTINUE statement in the WHILE loop is demonstrated in the following example. In this example, we'll assume that we wish to use a WHILE loop to <strong>print only odd values</strong> . The CONTINUE statement can be used to do this. This example will first <strong>test</strong> whether the variable value is <strong>odd or even</strong> . If it is even, the execution goes inside the IF…ELSE statement blocks and decrement the variable value by one. Then, it will execute the CONTINUE statement and starts a new iteration from the beginning.</p> <pre> DECLARE @Count INT SET @Count = 1 WHILE (@Count <= 1 2="0" 44 20) begin if @count % set + continue end print \'the odd value is=" + CONVERT(VARCHAR, @Count) SET @Count = @Count + 1 END </pre> <p>Executing the code snippet will display the below output:</p> <img src=" techcodeview.com img sql-server-tutorials sql-server-while-loop-6.webp\' alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <h3>How to implementing paging with WHILE loop in SQL Server?</h3> <p>We can also use the WHILE loop for implementing the paging. Paging allows displaying the subset of records from a table at any particular time. The following example will explain this concept. The WHILE loop in the code will select two records from the bikeshop table at a time. The records that have been chosen are then displayed in the output.</p> <pre> DECLARE @count INT DECLARE @limit INT; SET @count = 0 SET @limit = 2; WHILE @count <10 begin select * from bikeshop order by id offset @count rows fetch next @limit only set + 2; end; < pre> <p>Executing the code snippet will return the below output:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/sql-server-tutorials/44/sql-server-while-loop-7.webp" alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <h3>Nested WHILE Loop</h3> <p>The Nested WHILE Loop in SQL Server is simply a WHILE Loop written inside another WHILE Loop. When we work on multi-layered data, the Nested WHILE loops are essential. Because this concept is useful in extracting the layered data when we want to select them, it is recommended to be careful while using the nested loop.</p> <p> <strong>Syntax</strong> </p> <p>The following syntax illustrate the working of the nested WHILE Loop in SQL Server:</p> <pre> WHILE Expression BEGIN WHILE @Val2 <= 10 begin --second while loop statements sql end --this statement is outside the second --which first -- this < pre> <p>Let us explain this syntax step by step:</p> <p> <strong>Step 1:</strong> The loop starts by checking the first WHILE loop condition, and if it finds a false result, it will exit from While Loop. Otherwise, if the result is true, the control goes inside the BEGIN and END block for further execution. This block will start the execution of the second WHILE loop. See step 2.</p> <p> <strong>Step 2:</strong> This step will check the condition in the Nested WHILE Loop, and if it is false, the second loop will be exit and execute the statement outside this. Otherwise, if the result is true, the control goes inside the BEGIN and END block for further execution.</p> <p> <strong>Step 3:</strong> Once all the statements execute from the second WHILE loop, the control goes to the first WHILE and repeats the first step.</p> <p> <strong>Example</strong> </p> <p>The following example will print the multiplication table of 5 up to 10 using the nested WHILE loop.</p> <pre> DECLARE @val1 INT DECLARE @val2 INT SET @val1 = 5 SET @val2 = 1 WHILE @val1 <= 5 44 begin while @val2 <="10" print convert(varchar, @val1) + \' * @val2) techcodeview.com img sql-server-tutorials sql-server-while-loop-8.webp\' alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <h2>Conclusion</h2> <p>The WHILE loop is a useful method when there is a need to execute a SQL script repeatedly. The article explained how to work with the WHILE loop in MS SQL Server to execute operations such as record insertion and pagination with a simple example. Here we have also learned the BREAK and CONTINUE statements to control the WHILE loop iteration.</p> <hr></=></pre></=></pre></10></pre></=></pre></=>
הפעלת הקוד תציג את הפלט שלהלן:

ערך המשתנה מוערך לראשונה בקוד זה. אם הוא TRUE, הפקד נכנס ללולאה ומדפיס את ההצהרה. כאשר ערך המשתנה גדול או שווה ל-6, הפקד נכנס לבלוק IF...ELSE ומבצע את המשפט BREAK כדי לסיים את הלולאה. אם בלוק IF...ELSE לא מצליח לעמוד בתנאי; לאחר מכן, הלולאה תמשיך לפעול עד שהתנאי ישתנה ל-FALSE.
המשך הצהרה
SQL Server גם מאפשר לנו להשתמש במשפט CONTINUE בלולאת WHILE כמו שפות תכנות. הצהרה זו מיד מפסיק את הביצוע הנוכחי של הלולאה כאשר התנאי שצוין מתקיים , וזרימת הבקרה חוזרת לתחילת הלולאה. באופן כללי, ההצהרה IF...ELSE תשמש כדי לבדוק אם תנאי התקיים או לא.
המשפט CONTINUE בלולאת WHILE מודגם בדוגמה הבאה. בדוגמה זו, נניח שאנו רוצים להשתמש בלולאת WHILE כדי להדפיס רק ערכים אי-זוגיים . ניתן להשתמש במשפט CONTINUE לשם כך. דוגמה זו תחילה מִבְחָן האם ערך המשתנה הוא אי זוגי או זוגי . אם הוא זוגי, הביצוע נכנס לתוך בלוקים של המשפט IF…ELSE ומפחית את ערך המשתנה באחד. לאחר מכן, הוא יבצע את המשפט CONTINUE ויתחיל איטרציה חדשה מההתחלה.
regex ב-java
DECLARE @Count INT SET @Count = 1 WHILE (@Count <= 1 2="0" 44 20) begin if @count % set + continue end print \'the odd value is=" + CONVERT(VARCHAR, @Count) SET @Count = @Count + 1 END </pre> <p>Executing the code snippet will display the below output:</p> <img src=" techcodeview.com img sql-server-tutorials sql-server-while-loop-6.webp\' alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <h3>How to implementing paging with WHILE loop in SQL Server?</h3> <p>We can also use the WHILE loop for implementing the paging. Paging allows displaying the subset of records from a table at any particular time. The following example will explain this concept. The WHILE loop in the code will select two records from the bikeshop table at a time. The records that have been chosen are then displayed in the output.</p> <pre> DECLARE @count INT DECLARE @limit INT; SET @count = 0 SET @limit = 2; WHILE @count <10 begin select * from bikeshop order by id offset @count rows fetch next @limit only set + 2; end; < pre> <p>Executing the code snippet will return the below output:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/sql-server-tutorials/44/sql-server-while-loop-7.webp" alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <h3>Nested WHILE Loop</h3> <p>The Nested WHILE Loop in SQL Server is simply a WHILE Loop written inside another WHILE Loop. When we work on multi-layered data, the Nested WHILE loops are essential. Because this concept is useful in extracting the layered data when we want to select them, it is recommended to be careful while using the nested loop.</p> <p> <strong>Syntax</strong> </p> <p>The following syntax illustrate the working of the nested WHILE Loop in SQL Server:</p> <pre> WHILE Expression BEGIN WHILE @Val2 <= 10 begin --second while loop statements sql end --this statement is outside the second --which first -- this < pre> <p>Let us explain this syntax step by step:</p> <p> <strong>Step 1:</strong> The loop starts by checking the first WHILE loop condition, and if it finds a false result, it will exit from While Loop. Otherwise, if the result is true, the control goes inside the BEGIN and END block for further execution. This block will start the execution of the second WHILE loop. See step 2.</p> <p> <strong>Step 2:</strong> This step will check the condition in the Nested WHILE Loop, and if it is false, the second loop will be exit and execute the statement outside this. Otherwise, if the result is true, the control goes inside the BEGIN and END block for further execution.</p> <p> <strong>Step 3:</strong> Once all the statements execute from the second WHILE loop, the control goes to the first WHILE and repeats the first step.</p> <p> <strong>Example</strong> </p> <p>The following example will print the multiplication table of 5 up to 10 using the nested WHILE loop.</p> <pre> DECLARE @val1 INT DECLARE @val2 INT SET @val1 = 5 SET @val2 = 1 WHILE @val1 <= 5 44 begin while @val2 <="10" print convert(varchar, @val1) + \' * @val2) techcodeview.com img sql-server-tutorials sql-server-while-loop-8.webp\' alt="SQL Server WHILE LOOP"> <h2>Conclusion</h2> <p>The WHILE loop is a useful method when there is a need to execute a SQL script repeatedly. The article explained how to work with the WHILE loop in MS SQL Server to execute operations such as record insertion and pagination with a simple example. Here we have also learned the BREAK and CONTINUE statements to control the WHILE loop iteration.</p> <hr></=></pre></=></pre></10></pre></=>
