 #practiceLinkDiv { display: none !חשוב; }
#practiceLinkDiv { display: none !חשוב; }אלגוריתם מחיקה הפוכה קשור קשר הדוק אליו האלגוריתם של קרוסקל . באלגוריתם של Kruskal מה שאנחנו עושים זה: מיון קצוות לפי סדר הגדלת משקלם. לאחר המיון אנחנו אחד אחד בוחרים קצוות בסדר הולך וגדל. אנו כוללים קצה שנבחר נוכחי אם על ידי הכללת זה בעץ המתפרש לא יוצרים שום מחזור עד שיהיו קצוות V-1 בעץ המתפרש שבו V = מספר הקודקודים.
באלגוריתם Delete Reverse אנו ממיינים את כל הקצוות פּוֹחֵת סדר משקלם. לאחר המיון אנחנו אחד אחד בוחרים קצוות בסדר יורד. אָנוּ כלול קצה שנבחר אם לא כולל קצה זרם גורם לניתוק בגרף הנוכחי . הרעיון המרכזי הוא delete edge אם מחיקתו אינה מובילה לניתוק הגרף.
רשימת אתחול python
האלגוריתם:
- מיין את כל הקצוות של הגרף בסדר לא הולך וגדל של משקלי הקצוות.
- אתחול MST כגרף מקורי והסר קצוות נוספים באמצעות שלב 3.
- בחר את קצה המשקל הגבוה ביותר מהקצוות הנותרים ו בדוק אם מחיקת הקצה מנתקת את הגרף או לא .
אם מתנתקים אז אנחנו לא מוחקים את הקצה.
אחרת אנחנו מוחקים את הקצה וממשיכים.
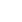
אִיוּר:
הבה נבין בעזרת הדוגמה הבאה:
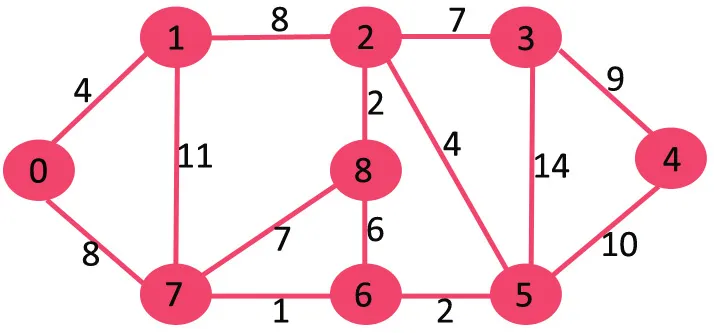
אם נמחק את קצה המשקל הגבוה ביותר של משקל 14 גרף לא יתנתק אז נסיר אותו.
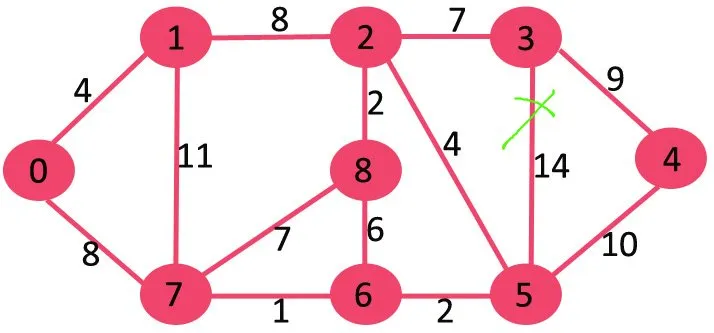
לאחר מכן אנו מוחקים 11 מכיוון שמחיקתו לא מנתקת את הגרף.
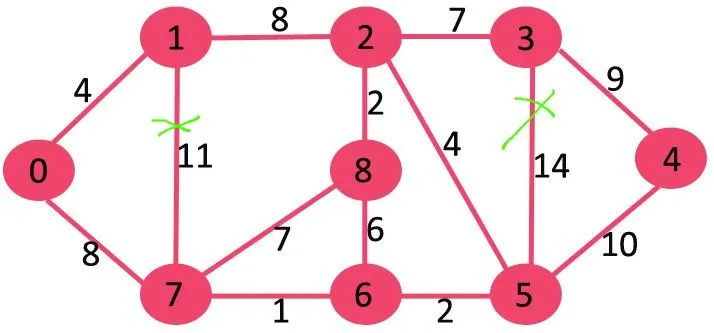
לאחר מכן אנו מוחקים 10 מכיוון שמחיקתו לא מנתקת את הגרף.

הבא הוא 9. אנחנו לא יכולים למחוק 9 מכיוון שמחיקתו גורמת לניתוק.

אנחנו ממשיכים בדרך זו והקצוות הבאים נשארים ב-MST הסופי.
Edges in MST
(3 4)
(0 7)
(2 3)
(2 5)
(0 1)
(5 6)
(2 8)
(6 7)
הערה: במקרה של קצוות משקל זהים נוכל לבחור כל קצה של אותם קצוות משקל.
תרגול מומלץ הפוך אלגוריתם מחיקה עבור עץ טווח מינימלי נסה את זה!יישום:
C++// C++ program to find Minimum Spanning Tree // of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm #include
// Java program to find Minimum Spanning Tree // of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm import java.util.*; // class to represent an edge class Edge implements Comparable<Edge> { int u v w; Edge(int u int v int w) { this.u = u; this.w = w; this.v = v; } public int compareTo(Edge other) { return (this.w - other.w); } } // Class to represent a graph using adjacency list // representation public class GFG { private int V; // No. of vertices private List<Integer>[] adj; private List<Edge> edges; @SuppressWarnings({ 'unchecked' 'deprecated' }) public GFG(int v) // Constructor { V = v; adj = new ArrayList[v]; for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) adj[i] = new ArrayList<Integer>(); edges = new ArrayList<Edge>(); } // function to Add an edge public void AddEdge(int u int v int w) { adj[u].add(v); // Add w to v’s list. adj[v].add(u); // Add w to v’s list. edges.add(new Edge(u v w)); } // function to perform dfs private void DFS(int v boolean[] visited) { // Mark the current node as visited and print it visited[v] = true; // Recur for all the vertices adjacent to // this vertex for (int i : adj[v]) { if (!visited[i]) DFS(i visited); } } // Returns true if given graph is connected else false private boolean IsConnected() { boolean[] visited = new boolean[V]; // Find all reachable vertices from first vertex DFS(0 visited); // If set of reachable vertices includes all // return true. for (int i = 1; i < V; i++) { if (visited[i] == false) return false; } return true; } // This function assumes that edge (u v) // exists in graph or not public void ReverseDeleteMST() { // Sort edges in increasing order on basis of cost Collections.sort(edges); int mst_wt = 0; // Initialize weight of MST System.out.println('Edges in MST'); // Iterate through all sorted edges in // decreasing order of weights for (int i = edges.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { int u = edges.get(i).u; int v = edges.get(i).v; // Remove edge from undirected graph adj[u].remove(adj[u].indexOf(v)); adj[v].remove(adj[v].indexOf(u)); // Adding the edge back if removing it // causes disconnection. In this case this // edge becomes part of MST. if (IsConnected() == false) { adj[u].add(v); adj[v].add(u); // This edge is part of MST System.out.println('(' + u + ' ' + v + ')'); mst_wt += edges.get(i).w; } } System.out.println('Total weight of MST is ' + mst_wt); } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { // create the graph given in above figure int V = 9; GFG g = new GFG(V); // making above shown graph g.AddEdge(0 1 4); g.AddEdge(0 7 8); g.AddEdge(1 2 8); g.AddEdge(1 7 11); g.AddEdge(2 3 7); g.AddEdge(2 8 2); g.AddEdge(2 5 4); g.AddEdge(3 4 9); g.AddEdge(3 5 14); g.AddEdge(4 5 10); g.AddEdge(5 6 2); g.AddEdge(6 7 1); g.AddEdge(6 8 6); g.AddEdge(7 8 7); g.ReverseDeleteMST(); } } // This code is contributed by Prithi_Dey
# Python3 program to find Minimum Spanning Tree # of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm # Graph class represents a directed graph # using adjacency list representation class Graph: def __init__(self v): # No. of vertices self.v = v self.adj = [0] * v self.edges = [] for i in range(v): self.adj[i] = [] # function to add an edge to graph def addEdge(self u: int v: int w: int): self.adj[u].append(v) # Add w to v’s list. self.adj[v].append(u) # Add w to v’s list. self.edges.append((w (u v))) def dfs(self v: int visited: list): # Mark the current node as visited and print it visited[v] = True # Recur for all the vertices adjacent to # this vertex for i in self.adj[v]: if not visited[i]: self.dfs(i visited) # Returns true if graph is connected # Returns true if given graph is connected else false def connected(self): visited = [False] * self.v # Find all reachable vertices from first vertex self.dfs(0 visited) # If set of reachable vertices includes all # return true. for i in range(1 self.v): if not visited[i]: return False return True # This function assumes that edge (u v) # exists in graph or not def reverseDeleteMST(self): # Sort edges in increasing order on basis of cost self.edges.sort(key = lambda a: a[0]) mst_wt = 0 # Initialize weight of MST print('Edges in MST') # Iterate through all sorted edges in # decreasing order of weights for i in range(len(self.edges) - 1 -1 -1): u = self.edges[i][1][0] v = self.edges[i][1][1] # Remove edge from undirected graph self.adj[u].remove(v) self.adj[v].remove(u) # Adding the edge back if removing it # causes disconnection. In this case this # edge becomes part of MST. if self.connected() == False: self.adj[u].append(v) self.adj[v].append(u) # This edge is part of MST print('( %d %d )' % (u v)) mst_wt += self.edges[i][0] print('Total weight of MST is' mst_wt) # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': # create the graph given in above figure V = 9 g = Graph(V) # making above shown graph g.addEdge(0 1 4) g.addEdge(0 7 8) g.addEdge(1 2 8) g.addEdge(1 7 11) g.addEdge(2 3 7) g.addEdge(2 8 2) g.addEdge(2 5 4) g.addEdge(3 4 9) g.addEdge(3 5 14) g.addEdge(4 5 10) g.addEdge(5 6 2) g.addEdge(6 7 1) g.addEdge(6 8 6) g.addEdge(7 8 7) g.reverseDeleteMST() # This code is contributed by # sanjeev2552
// C# program to find Minimum Spanning Tree // of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm using System; using System.Collections.Generic; // class to represent an edge public class Edge : IComparable<Edge> { public int u v w; public Edge(int u int v int w) { this.u = u; this.v = v; this.w = w; } public int CompareTo(Edge other) { return this.w.CompareTo(other.w); } } // Graph class represents a directed graph // using adjacency list representation public class Graph { private int V; // No. of vertices private List<int>[] adj; private List<Edge> edges; public Graph(int v) // Constructor { V = v; adj = new List<int>[ v ]; for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) adj[i] = new List<int>(); edges = new List<Edge>(); } // function to Add an edge public void AddEdge(int u int v int w) { adj[u].Add(v); // Add w to v’s list. adj[v].Add(u); // Add w to v’s list. edges.Add(new Edge(u v w)); } // function to perform dfs private void DFS(int v bool[] visited) { // Mark the current node as visited and print it visited[v] = true; // Recur for all the vertices adjacent to // this vertex foreach(int i in adj[v]) { if (!visited[i]) DFS(i visited); } } // Returns true if given graph is connected else false private bool IsConnected() { bool[] visited = new bool[V]; // Find all reachable vertices from first vertex DFS(0 visited); // If set of reachable vertices includes all // return true. for (int i = 1; i < V; i++) { if (visited[i] == false) return false; } return true; } // This function assumes that edge (u v) // exists in graph or not public void ReverseDeleteMST() { // Sort edges in increasing order on basis of cost edges.Sort(); int mst_wt = 0; // Initialize weight of MST Console.WriteLine('Edges in MST'); // Iterate through all sorted edges in // decreasing order of weights for (int i = edges.Count - 1; i >= 0; i--) { int u = edges[i].u; int v = edges[i].v; // Remove edge from undirected graph adj[u].Remove(v); adj[v].Remove(u); // Adding the edge back if removing it // causes disconnection. In this case this // edge becomes part of MST. if (IsConnected() == false) { adj[u].Add(v); adj[v].Add(u); // This edge is part of MST Console.WriteLine('({0} {1})' u v); mst_wt += edges[i].w; } } Console.WriteLine('Total weight of MST is {0}' mst_wt); } } class GFG { // Driver code static void Main(string[] args) { // create the graph given in above figure int V = 9; Graph g = new Graph(V); // making above shown graph g.AddEdge(0 1 4); g.AddEdge(0 7 8); g.AddEdge(1 2 8); g.AddEdge(1 7 11); g.AddEdge(2 3 7); g.AddEdge(2 8 2); g.AddEdge(2 5 4); g.AddEdge(3 4 9); g.AddEdge(3 5 14); g.AddEdge(4 5 10); g.AddEdge(5 6 2); g.AddEdge(6 7 1); g.AddEdge(6 8 6); g.AddEdge(7 8 7); g.ReverseDeleteMST(); } } // This code is contributed by cavi4762
// Javascript program to find Minimum Spanning Tree // of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm // Graph class represents a directed graph // using adjacency list representation class Graph { // Constructor constructor(V) { this.V = V; this.adj = []; this.edges = []; for (let i = 0; i < V; i++) { this.adj[i] = []; } } // function to add an edge to graph addEdge(u v w) { this.adj[u].push(v);// Add w to v’s list. this.adj[v].push(u);// Add w to v’s list. this.edges.push([w [u v]]); } DFS(v visited) { // Mark the current node as visited and print it visited[v] = true; for (const i of this.adj[v]) { if (!visited[i]) { this.DFS(i visited); } } } // Returns true if given graph is connected else false isConnected() { const visited = []; for (let i = 0; i < this.V; i++) { visited[i] = false; } // Find all reachable vertices from first vertex this.DFS(0 visited); // If set of reachable vertices includes all // return true. for (let i = 1; i < this.V; i++) { if (!visited[i]) { return false; } } return true; } // This function assumes that edge (u v) // exists in graph or not reverseDeleteMST() { // Sort edges in increasing order on basis of cost this.edges.sort((a b) => a[0] - b[0]); let mstWt = 0;// Initialize weight of MST console.log('Edges in MST'); // Iterate through all sorted edges in // decreasing order of weights for (let i = this.edges.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { const [u v] = this.edges[i][1]; // Remove edge from undirected graph this.adj[u] = this.adj[u].filter(x => x !== v); this.adj[v] = this.adj[v].filter(x => x !== u); // Adding the edge back if removing it // causes disconnection. In this case this // edge becomes part of MST. if (!this.isConnected()) { this.adj[u].push(v); this.adj[v].push(u); // This edge is part of MST console.log(`(${u} ${v})`); mstWt += this.edges[i][0]; } } console.log(`Total weight of MST is ${mstWt}`); } } // Driver code function main() { // create the graph given in above figure var V = 9; var g = new Graph(V); // making above shown graph g.addEdge(0 1 4); g.addEdge(0 7 8); g.addEdge(1 2 8); g.addEdge(1 7 11); g.addEdge(2 3 7); g.addEdge(2 8 2); g.addEdge(2 5 4); g.addEdge(3 4 9); g.addEdge(3 5 14); g.addEdge(4 5 10); g.addEdge(5 6 2); g.addEdge(6 7 1); g.addEdge(6 8 6); g.addEdge(7 8 7); g.reverseDeleteMST(); } main();
תְפוּקָה
Edges in MST (3 4) (0 7) (2 3) (2 5) (0 1) (5 6) (2 8) (6 7) Total weight of MST is 37
מורכבות הזמן: O((E*(V+E)) + E log E) כאשר E הוא מספר הקצוות.
מורכבות החלל: O(V+E) כאשר V הוא מספר הקודקודים ו-E הוא מספר הקצוות. אנו משתמשים ברשימת סמיכות כדי לאחסן את הגרף ולכן אנו זקוקים לרווח פרופורציונלי ל-O(V+E).
הערות:
כיצד להמיר מחרוזת למספר שלם ב-java
- המימוש לעיל הוא יישום פשוט/נאיבי של אלגוריתם מחיקה הפוכה וניתן לבצע אופטימיזציה ל-O(E log V (log log V)3) [מקור: שבוע ]. אבל מורכבות הזמן האופטימלית הזו עדיין קטנה מ מִצטַנֵעַ ו קרוסקל אלגוריתמים עבור MST.
- היישום לעיל משנה את הגרף המקורי. אנו יכולים ליצור עותק של הגרף אם יש לשמור על הגרף המקורי.
צור חידון
