ה עבור לולאה בשפת C משמש כדי לחזור על ההצהרות או חלק מהתוכנית מספר פעמים. הוא משמש לעתים קרובות כדי לעבור בין מבני הנתונים כמו המערך והרשימה המקושרת.
תחביר של for loop ב-C
התחביר של for loop בשפת c ניתן להלן:
javatable
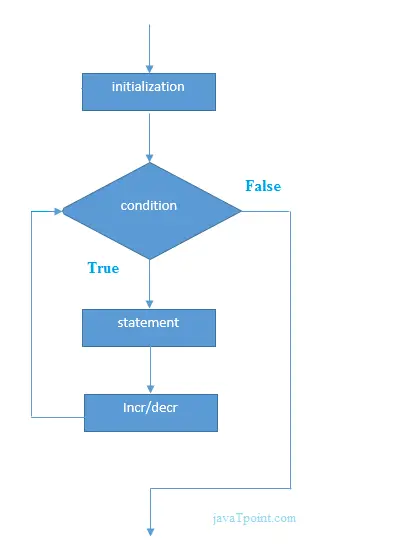
for(Expression 1; Expression 2; Expression 3){ //code to be executed } תרשים זרימה של for loop ב-C
C עבור לולאה דוגמאות
בוא נראה את התוכנית הפשוטה של for loop שמדפיסה טבלה של 1.
#include int main(){ int i=0; for(i=1;i<=10;i++){ printf('%d
',i); } return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 </pre> <h3>C Program: Print table for the given number using C for loop</h3> <pre> #include int main(){ int i=1,number=0; printf('Enter a number: '); scanf('%d',&number); for(i=1;i<=10;i++){ printf('%d
',(number*i)); } return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> Enter a number: 2 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 </pre> <pre> Enter a number: 1000 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 9000 10000 </pre> <h3>Properties of Expression 1</h3> <ul> <li>The expression represents the initialization of the loop variable.</li> <li>We can initialize more than one variable in Expression 1.</li> <li>Expression 1 is optional.</li> <li>In C, we can not declare the variables in Expression 1. However, It can be an exception in some compilers.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int a,b,c; for(a=0,b=12,c=23;a<2;a++) { printf('%d ',a+b+c); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 35 36 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 2</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i=1; for(;i<5;i++) { printf('%d ',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 1 2 3 4 </pre> <h3>Properties of Expression 2</h3> <ul> <li>Expression 2 is a conditional expression. It checks for a specific condition to be satisfied. If it is not, the loop is terminated.</li> <li>Expression 2 can have more than one condition. However, the loop will iterate until the last condition becomes false. Other conditions will be treated as statements.</li> <li>Expression 2 is optional.</li> <li>Expression 2 can perform the task of expression 1 and expression 3. That is, we can initialize the variable as well as update the loop variable in expression 2 itself.</li> <li>We can pass zero or non-zero value in expression 2. However, in C, any non-zero value is true, and zero is false by default.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;i<=4;i++) { printf('%d ',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 1 2 3 4 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 2</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i,j,k; for(i=0,j=0,k=0;i<4,k<8,j<10;i++) { printf('%d %d %d
',i,j,k); j+="2;" k+="3;" } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 0 0 1 2 3 2 4 6 3 6 9 4 8 12 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 3</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;;i++) { printf('%d',i); } } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> infinite loop </pre> <h4>Properties of Expression 3 <ul> <li>Expression 3 is used to update the loop variable.</li> <li>We can update more than one variable at the same time.</li> <li>Expression 3 is optional.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include void main () { int i=0,j=2; for(i = 0;i<5;i++,j=j+2) { printf('%d %d
',i,j); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> <pre> 0 2 1 4 2 6 3 8 4 10 </pre> </p><h3>Loop body</h3> <p>The braces {} are used to define the scope of the loop. However, if the loop contains only one statement, then we don't need to use braces. A loop without a body is possible. The braces work as a block separator, i.e., the value variable declared inside for loop is valid only for that block and not outside. Consider the following example.</p> <pre> #include void main () { int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { int i="20;" printf('%d ',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 </pre> <h3>Infinitive for loop in C</h3> <p>To make a for loop infinite, we need not give any expression in the syntax. Instead of that, we need to provide two semicolons to validate the syntax of the for loop. This will work as an infinite for loop.</p> <pre> #include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } </pre> <p>If you run this program, you will see above statement infinite times.</p> <hr></10;i++)></pre></5;i++,j=j+2)></pre></h4></4,k<8,j<10;i++)></pre></=4;i++)></pre></5;i++)></pre></2;a++)></pre></=10;i++){></pre></=10;i++){> תוכנית C: הדפס טבלה עבור המספר הנתון באמצעות C עבור לולאה
#include int main(){ int i=1,number=0; printf('Enter a number: '); scanf('%d',&number); for(i=1;i<=10;i++){ printf(\'%d
\',(number*i)); } return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> Enter a number: 2 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 </pre> <pre> Enter a number: 1000 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 9000 10000 </pre> <h3>Properties of Expression 1</h3> <ul> <li>The expression represents the initialization of the loop variable.</li> <li>We can initialize more than one variable in Expression 1.</li> <li>Expression 1 is optional.</li> <li>In C, we can not declare the variables in Expression 1. However, It can be an exception in some compilers.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int a,b,c; for(a=0,b=12,c=23;a<2;a++) { printf(\'%d \',a+b+c); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 35 36 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 2</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i=1; for(;i<5;i++) { printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 1 2 3 4 </pre> <h3>Properties of Expression 2</h3> <ul> <li>Expression 2 is a conditional expression. It checks for a specific condition to be satisfied. If it is not, the loop is terminated.</li> <li>Expression 2 can have more than one condition. However, the loop will iterate until the last condition becomes false. Other conditions will be treated as statements.</li> <li>Expression 2 is optional.</li> <li>Expression 2 can perform the task of expression 1 and expression 3. That is, we can initialize the variable as well as update the loop variable in expression 2 itself.</li> <li>We can pass zero or non-zero value in expression 2. However, in C, any non-zero value is true, and zero is false by default.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;i<=4;i++) { printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 1 2 3 4 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 2</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i,j,k; for(i=0,j=0,k=0;i<4,k<8,j<10;i++) { printf(\'%d %d %d
\',i,j,k); j+="2;" k+="3;" } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 0 0 1 2 3 2 4 6 3 6 9 4 8 12 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 3</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;;i++) { printf('%d',i); } } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> infinite loop </pre> <h4>Properties of Expression 3 <ul> <li>Expression 3 is used to update the loop variable.</li> <li>We can update more than one variable at the same time.</li> <li>Expression 3 is optional.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include void main () { int i=0,j=2; for(i = 0;i<5;i++,j=j+2) { printf(\'%d %d
\',i,j); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> <pre> 0 2 1 4 2 6 3 8 4 10 </pre> </p><h3>Loop body</h3> <p>The braces {} are used to define the scope of the loop. However, if the loop contains only one statement, then we don't need to use braces. A loop without a body is possible. The braces work as a block separator, i.e., the value variable declared inside for loop is valid only for that block and not outside. Consider the following example.</p> <pre> #include void main () { int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { int i="20;" printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 </pre> <h3>Infinitive for loop in C</h3> <p>To make a for loop infinite, we need not give any expression in the syntax. Instead of that, we need to provide two semicolons to validate the syntax of the for loop. This will work as an infinite for loop.</p> <pre> #include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } </pre> <p>If you run this program, you will see above statement infinite times.</p> <hr></10;i++)></pre></5;i++,j=j+2)></pre></h4></4,k<8,j<10;i++)></pre></=4;i++)></pre></5;i++)></pre></2;a++)></pre></=10;i++){> Enter a number: 1000 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 9000 10000
מאפייני ביטוי 1
- הביטוי מייצג את האתחול של משתנה הלולאה.
- אנו יכולים לאתחל יותר ממשתנה אחד בביטוי 1.
- ביטוי 1 הוא אופציונלי.
- ב-C, אנחנו לא יכולים להכריז על המשתנים בביטוי 1. עם זאת, זה יכול להיות חריג בחלק מהמהדרים.
דוגמה 1
#include int main() { int a,b,c; for(a=0,b=12,c=23;a<2;a++) { printf(\'%d \',a+b+c); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 35 36 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 2</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i=1; for(;i<5;i++) { printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 1 2 3 4 </pre> <h3>Properties of Expression 2</h3> <ul> <li>Expression 2 is a conditional expression. It checks for a specific condition to be satisfied. If it is not, the loop is terminated.</li> <li>Expression 2 can have more than one condition. However, the loop will iterate until the last condition becomes false. Other conditions will be treated as statements.</li> <li>Expression 2 is optional.</li> <li>Expression 2 can perform the task of expression 1 and expression 3. That is, we can initialize the variable as well as update the loop variable in expression 2 itself.</li> <li>We can pass zero or non-zero value in expression 2. However, in C, any non-zero value is true, and zero is false by default.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;i<=4;i++) { printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 1 2 3 4 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 2</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i,j,k; for(i=0,j=0,k=0;i<4,k<8,j<10;i++) { printf(\'%d %d %d
\',i,j,k); j+="2;" k+="3;" } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 0 0 1 2 3 2 4 6 3 6 9 4 8 12 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 3</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;;i++) { printf('%d',i); } } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> infinite loop </pre> <h4>Properties of Expression 3 <ul> <li>Expression 3 is used to update the loop variable.</li> <li>We can update more than one variable at the same time.</li> <li>Expression 3 is optional.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include void main () { int i=0,j=2; for(i = 0;i<5;i++,j=j+2) { printf(\'%d %d
\',i,j); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> <pre> 0 2 1 4 2 6 3 8 4 10 </pre> </p><h3>Loop body</h3> <p>The braces {} are used to define the scope of the loop. However, if the loop contains only one statement, then we don't need to use braces. A loop without a body is possible. The braces work as a block separator, i.e., the value variable declared inside for loop is valid only for that block and not outside. Consider the following example.</p> <pre> #include void main () { int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { int i="20;" printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 </pre> <h3>Infinitive for loop in C</h3> <p>To make a for loop infinite, we need not give any expression in the syntax. Instead of that, we need to provide two semicolons to validate the syntax of the for loop. This will work as an infinite for loop.</p> <pre> #include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } </pre> <p>If you run this program, you will see above statement infinite times.</p> <hr></10;i++)></pre></5;i++,j=j+2)></pre></h4></4,k<8,j<10;i++)></pre></=4;i++)></pre></5;i++)></pre></2;a++)> דוגמה 2
#include int main() { int i=1; for(;i<5;i++) { printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 1 2 3 4 </pre> <h3>Properties of Expression 2</h3> <ul> <li>Expression 2 is a conditional expression. It checks for a specific condition to be satisfied. If it is not, the loop is terminated.</li> <li>Expression 2 can have more than one condition. However, the loop will iterate until the last condition becomes false. Other conditions will be treated as statements.</li> <li>Expression 2 is optional.</li> <li>Expression 2 can perform the task of expression 1 and expression 3. That is, we can initialize the variable as well as update the loop variable in expression 2 itself.</li> <li>We can pass zero or non-zero value in expression 2. However, in C, any non-zero value is true, and zero is false by default.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;i<=4;i++) { printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 1 2 3 4 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 2</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i,j,k; for(i=0,j=0,k=0;i<4,k<8,j<10;i++) { printf(\'%d %d %d
\',i,j,k); j+="2;" k+="3;" } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 0 0 1 2 3 2 4 6 3 6 9 4 8 12 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 3</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;;i++) { printf('%d',i); } } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> infinite loop </pre> <h4>Properties of Expression 3 <ul> <li>Expression 3 is used to update the loop variable.</li> <li>We can update more than one variable at the same time.</li> <li>Expression 3 is optional.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include void main () { int i=0,j=2; for(i = 0;i<5;i++,j=j+2) { printf(\'%d %d
\',i,j); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> <pre> 0 2 1 4 2 6 3 8 4 10 </pre> </p><h3>Loop body</h3> <p>The braces {} are used to define the scope of the loop. However, if the loop contains only one statement, then we don't need to use braces. A loop without a body is possible. The braces work as a block separator, i.e., the value variable declared inside for loop is valid only for that block and not outside. Consider the following example.</p> <pre> #include void main () { int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { int i="20;" printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 </pre> <h3>Infinitive for loop in C</h3> <p>To make a for loop infinite, we need not give any expression in the syntax. Instead of that, we need to provide two semicolons to validate the syntax of the for loop. This will work as an infinite for loop.</p> <pre> #include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } </pre> <p>If you run this program, you will see above statement infinite times.</p> <hr></10;i++)></pre></5;i++,j=j+2)></pre></h4></4,k<8,j<10;i++)></pre></=4;i++)></pre></5;i++)> מאפייני ביטוי 2
- ביטוי 2 הוא ביטוי מותנה. הוא בודק אם קיים תנאי ספציפי. אם לא, הלולאה מסתיימת.
- לביטוי 2 יכול להיות יותר מתנאי אחד. עם זאת, הלולאה תחזור על עצמה עד שהתנאי האחרון יהפוך לשווא. תנאים אחרים יטופלו כהצהרות.
- ביטוי 2 הוא אופציונלי.
- ביטוי 2 יכול לבצע את המשימה של ביטוי 1 וביטוי 3. כלומר, אנו יכולים לאתחל את המשתנה וכן לעדכן את משתנה הלולאה בביטוי 2 עצמו.
- אנו יכולים להעביר ערך אפס או לא אפס בביטוי 2. עם זאת, ב-C, כל ערך שאינו אפס הוא אמת, ואפס הוא שקר כברירת מחדל.
דוגמה 1
כיצד להפנות מצביע ב-c
#include int main() { int i; for(i=0;i<=4;i++) { printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 1 2 3 4 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 2</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i,j,k; for(i=0,j=0,k=0;i<4,k<8,j<10;i++) { printf(\'%d %d %d
\',i,j,k); j+="2;" k+="3;" } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 0 0 1 2 3 2 4 6 3 6 9 4 8 12 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 3</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;;i++) { printf('%d',i); } } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> infinite loop </pre> <h4>Properties of Expression 3 <ul> <li>Expression 3 is used to update the loop variable.</li> <li>We can update more than one variable at the same time.</li> <li>Expression 3 is optional.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include void main () { int i=0,j=2; for(i = 0;i<5;i++,j=j+2) { printf(\'%d %d
\',i,j); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> <pre> 0 2 1 4 2 6 3 8 4 10 </pre> </p><h3>Loop body</h3> <p>The braces {} are used to define the scope of the loop. However, if the loop contains only one statement, then we don't need to use braces. A loop without a body is possible. The braces work as a block separator, i.e., the value variable declared inside for loop is valid only for that block and not outside. Consider the following example.</p> <pre> #include void main () { int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { int i="20;" printf(\'%d \',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 </pre> <h3>Infinitive for loop in C</h3> <p>To make a for loop infinite, we need not give any expression in the syntax. Instead of that, we need to provide two semicolons to validate the syntax of the for loop. This will work as an infinite for loop.</p> <pre> #include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } </pre> <p>If you run this program, you will see above statement infinite times.</p> <hr></10;i++)></pre></5;i++,j=j+2)></pre></h4></4,k<8,j<10;i++)></pre></=4;i++)> דוגמה 2
#include int main() { int i,j,k; for(i=0,j=0,k=0;i<4,k<8,j<10;i++) { printf(\\'%d %d %d
\\',i,j,k); j+="2;" k+="3;" } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 0 0 0 1 2 3 2 4 6 3 6 9 4 8 12 </pre> <p> <strong>Example 3</strong> </p> <pre> #include int main() { int i; for(i=0;;i++) { printf('%d',i); } } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> infinite loop </pre> <h4>Properties of Expression 3 <ul> <li>Expression 3 is used to update the loop variable.</li> <li>We can update more than one variable at the same time.</li> <li>Expression 3 is optional.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Example 1</strong> </p> <pre> #include void main () { int i=0,j=2; for(i = 0;i<5;i++,j=j+2) { printf(\\'%d %d
\\',i,j); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> <pre> 0 2 1 4 2 6 3 8 4 10 </pre> </p><h3>Loop body</h3> <p>The braces {} are used to define the scope of the loop. However, if the loop contains only one statement, then we don't need to use braces. A loop without a body is possible. The braces work as a block separator, i.e., the value variable declared inside for loop is valid only for that block and not outside. Consider the following example.</p> <pre> #include void main () { int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { int i="20;" printf(\\'%d \\',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 </pre> <h3>Infinitive for loop in C</h3> <p>To make a for loop infinite, we need not give any expression in the syntax. Instead of that, we need to provide two semicolons to validate the syntax of the for loop. This will work as an infinite for loop.</p> <pre> #include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } </pre> <p>If you run this program, you will see above statement infinite times.</p> <hr></10;i++)></pre></5;i++,j=j+2)></pre></h4></4,k<8,j<10;i++)> דוגמה 3
#include int main() { int i; for(i=0;;i++) { printf('%d',i); } } תְפוּקָה
infinite loop
מאפייני ביטוי 3 - ביטוי 3 משמש לעדכון משתנה הלולאה.
- אנו יכולים לעדכן יותר ממשתנה אחד בו-זמנית.
- ביטוי 3 הוא אופציונלי.
דוגמה 1
הורד סרטוני יוטיוב vlc
#include void main () { int i=0,j=2; for(i = 0;i<5;i++,j=j+2) { printf(\\'%d %d
\\',i,j); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> <pre> 0 2 1 4 2 6 3 8 4 10 </pre> </p><h3>Loop body</h3> <p>The braces {} are used to define the scope of the loop. However, if the loop contains only one statement, then we don't need to use braces. A loop without a body is possible. The braces work as a block separator, i.e., the value variable declared inside for loop is valid only for that block and not outside. Consider the following example.</p> <pre> #include void main () { int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { int i="20;" printf(\\'%d \\',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 </pre> <h3>Infinitive for loop in C</h3> <p>To make a for loop infinite, we need not give any expression in the syntax. Instead of that, we need to provide two semicolons to validate the syntax of the for loop. This will work as an infinite for loop.</p> <pre> #include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } </pre> <p>If you run this program, you will see above statement infinite times.</p> <hr></10;i++)></pre></5;i++,j=j+2)> גוף לולאה
הסוגרים {} משמשים להגדרת היקף הלולאה. עם זאת, אם הלולאה מכילה רק משפט אחד, אז איננו צריכים להשתמש בסוגריים. לולאה ללא גוף אפשרית. הפלטה פועלת כמפריד בלוק, כלומר, משתנה הערך המוצהר בתוך לולאה תקף רק עבור הבלוק הזה ולא מחוצה לו. שקול את הדוגמה הבאה.
#include void main () { int i; for(i=0;i<10;i++) { int i="20;" printf(\\'%d \\',i); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <pre> 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 </pre> <h3>Infinitive for loop in C</h3> <p>To make a for loop infinite, we need not give any expression in the syntax. Instead of that, we need to provide two semicolons to validate the syntax of the for loop. This will work as an infinite for loop.</p> <pre> #include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } </pre> <p>If you run this program, you will see above statement infinite times.</p> <hr></10;i++)> אינפיניטי עבור לולאה ב-C
כדי להפוך לולאת for אינסופית, אנחנו לא צריכים לתת שום ביטוי בתחביר. במקום זאת, עלינו לספק שני נקודות פסיק כדי לאמת את התחביר של לולאת for. זה יעבוד בתור לולאה אינסופית.
#include void main () { for(;;) { printf('welcome to javatpoint'); } } אם תפעיל תוכנית זו, תראה את ההצהרה שלמעלה אינסוף פעמים.
