Python היא שפת תכנות תלוית רישיות, כלומר, השפה מתייחסת לתווים גדולים וקטנים בצורה שונה. לדוגמה, ב-Python, המשתנה 'x' אינו זהה למשתנה 'X'. התנהגות זו שונה משפות תכנות אחרות, כגון JavaScript, שאינן תלויות רישיות.
int למחרוזת
ב-Python, שמות משתנים, שמות פונקציות ומילות מפתח הם כולם תלויי רישיות. זה אומר שאם תגדיר משתנה 'x' ואז תנסה להתייחס אליו מאוחר יותר בתור 'X', Python יתייחס אליו כמשתנה אחר, ותקבל שגיאה. באופן דומה, אם תנסה לקרוא לפונקציה 'הדפסה' במקום 'הדפס', Python גם ייתן לך שגיאה.
הנה דוגמה לאופן שבו רגישות רישיות משפיעה על שמות משתנים ב-Python:
x = 5 X = 10 print(x) # Output: 5 print(X) # Output: 10
תְפוּקָה
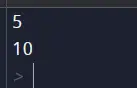
הֶסבֵּר:
בדוגמה זו, הגדרנו שני משתנים, 'x' ו-'X' עם ערכים שונים. כאשר אנו מדפיסים אותם, אנו רואים ש-Python מתייחס אליהם כמשתנים נפרדים ומקצה להם ערכים שונים.
רגישות רישיות חלה גם על שמות פונקציות ב- Python. לדוגמה:
מחסנית ב-ds
print('Hello, World!') # Output: Hello, World! Print('Hello, World!') # Output: NameError: name 'Print' is not defined
תְפוּקָה

הֶסבֵּר:
הפונקציה המובנית 'print()' שונה מהפונקציה 'Print()'. הראשון יעבוד כצפוי, בעוד שהאחרון ייתן שגיאה כי זו לא פונקציה מוגדרת.
מילות מפתח ב-Python הן גם תלויות רישיות. המשמעות היא שאם אתה משתמש במילת מפתח כגון 'אם' או 'עבור' באותיות קטנות, היא תעבוד כצפוי. עם זאת, אם אתה משתמש בו באותיות רישיות, Python יתייחס אליו כשם משתנה ותקבל שגיאה.
קוד מקור:
מחרוזת משנה java מכילה
if x <10: print('x is less than 10') if x < 10: # output: nameerror: name 'if' not defined pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/48/is-python-case-sensitive-3.webp" alt="Is Python Case Sensitive"> <p> <strong>Explanation:</strong> </p> <p>In the above code, we have created two if statements. In the first if statement, we have used the proper syntax as Python is case-sensitive. We have created the first if statement with small i, and the second if statement has a capital I which means it is not correct syntax, so it will throw an error.</p> <p>In addition to variable names, function names, and keywords, Python is also case-sensitive when it comes to file names. This means that the file 'example.txt' is different from the file 'Example.txt,' and the interpreter will treat them as separate files.</p> <p>It is important to keep in mind that Python is case-sensitive when naming variables, functions, and keywords. This can lead to errors and unexpected behavior if you're not careful. To avoid these issues, it is a good practice to use a consistent naming convention, such as using lowercase letters for all variable and function names.</p> <p>In conclusion, Python is a case-sensitive programming language. This means that the language treats uppercase and lowercase characters differently. This applies to variable names, function names, keywords, and file names. It's important to keep in mind that case sensitivity can lead to errors and unexpected behavior if you're not careful, so it's a good practice to use a consistent naming convention.</p> <hr></10:>